Croatian Humanists, Ecumenists, Latinists, and Encyclopaedists
© by Darko Zubrinic, Zagreb (1995)Contents:
Croats at European universities in the Middle Ages
The first public schools in Croatia were founded in Zadar (1282), Dubrovnik (1333) and Zagreb (1362). The first Gymnasium was founded by Paulists in Lepoglava near Zagreb in 1503. 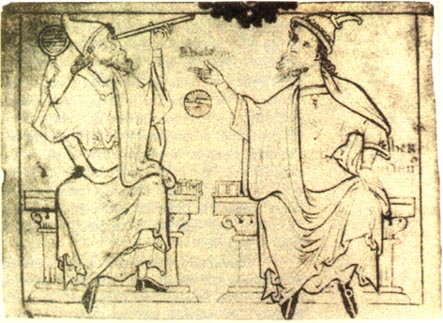 Croatian
students studied at many
European
Universities, starting from the Early Middle Ages. For example, Herman
Dalmatin (1110-1154) was our
first student who attended lectures of
the famous Thierry de Chartres in Paris in the thirties of the 12th
century. Born according to his own words in the heart of Istria, he
wrote about 20 original books and translations, thus contributing a
great deal to natural philosophy and exact sciences in Europe. He
travelled a lot, and besides Latin and Greek mastered perfectly Arabic.
Croatian
students studied at many
European
Universities, starting from the Early Middle Ages. For example, Herman
Dalmatin (1110-1154) was our
first student who attended lectures of
the famous Thierry de Chartres in Paris in the thirties of the 12th
century. Born according to his own words in the heart of Istria, he
wrote about 20 original books and translations, thus contributing a
great deal to natural philosophy and exact sciences in Europe. He
travelled a lot, and besides Latin and Greek mastered perfectly Arabic.
On
the left you can see an old drawing of Herman
with an astrolabe in his hand, shown with Euclid (from Chronica Maiora
written by Matthew of Paris in the 13th century). See a monograph by
Zarko Dadic - Herman of
Dalmatia, Skolska knjiga,
Zagreb, 212
pp (parallel English and Croatian text).
He translated many important books from Arabian into Latin, like Euclid's Elements, Al-Khwarizmi's Tables (continuing the work of Adelard of Bath on both classics), Sahl ibn Bishr's (Arabian scientist of the Jewish origin, 9th century) Sextus astronomicae liber, Abu-Ma'ashar's Introduction to Astronomy, acquainting thus the West with Aristotel's thoughts, and in particular the oldest Latin redaction of Ptolomey's Planisphere (published in Toulouse 1143; in Islamic literature known as `Almagest'). Herman wrote an astrological - cosmological treatise De essentiis (Béziers, 1143). With his English friend Robert from Ketton he worked on the translation of Kur'an. Herman's translations from Arabic represent an unavoidable ingredient of the so-called `Toledo corpus' of texts on Islam. Its main objective was to resist Islam not by force as the Crusaders did, but by understanding and love. As we know, the Arabic culture was a bridge across which the spiritual heritage of the Ancient Greeks came to the West.
The Croats were also present at the Court of the Andalusian califs in Cordoba (Spain). The body guard for califs was composed of islamized Croats. Among them the most famous were Wadha el-Ameri and Zahair Alameri (11th century). The Croatian kingdom maintained relations with the Califat, so that in 953 the Croatian legation visited Cordoba.
The oldest known map where the name of Croatia appears is El'Idrisi's map of the Mediterranean sea from 1154. The name of Croatia is written as Garuasia. This map was a supplement of El'Idrisi's book "The Joy of Those Who Long to Travel around the World".


Pavao Dalmatin (1190-1255), a professor at the University of Bologna, a founder of the first Dominican communities in Croatia and Hungary, wrote the first systematic tractate on confession in the history of Catholic theology ("Summa de confessione"). Its last edition was printed in 1919 in Dutch.
Augustin Kazotic, a Dominican from the beautiful city of Trogir (13th century), the future bishop of Zagreb, studied at the University of Paris (Sorbonne) by the end of the 13th century. He was reputed to be "an excellent orator and brilliant diplomat" not only in Croatia, but also in France and Italy. He also founded the important Library of Metropolitana in Zagreb, existing continuously from 13th century to these days. Beatified in 1702.
It seems that Dante traveled through Croatia, and with help of Croatian pilgrim, now a friend and guide through Croatia, Bishop Kazotic, he visited Jurandvor on the island of Krk and saw the Baska Tablet.

Also very old and important are the
- the Library of Dominicans in Dubrovnik (founded in 13th century, shelled by the Serbs in 1991/1992),
- the grand Library of Paulists in Lepoglava (confiscated after the Austrians cancelled the Paulist order in 1786 - a tremendous loss for Croatian culture).
The first known Croatian student of the Charles University in Prague (founded in 1348) was fra Ilija from Dubrovnik, starting from 1391. The famous Czech king Charles IV of Luxemburg built a Glagolitic convent in Prague in 1347, where Croatian Benedictines from the island of Pasman were invited as teachers. It is remarkable that the convent was just a few hundred meters from the Charles University.
The first Croatian rector of the University of Padova was elected for the period of 1397/1398. On the Faculty of Law and the Faculty of Artists of the same University we know of dozens of Croatian rectors and prorectors from the 14th century onwards. It would be difficult even to count the number of Croatian students at the University of Padova. Some of them became lecturers there, like Frederik Grisogono and Mark Antun de Dominis.
In the fifteenth century several Croats were professors at the University of Paris: Pavao Nikolin, Ivan Stojkovic, Petar Gucetic and others.
Georges d'Esclavonie (or de Sorbonne, Juraj Slovinac, born in Brezice in present Slovenia, 1355/60-1416), a professor at the University of Paris (Sorbonne) and a theological writer, wrote the first Croatian abecedarium of Christian science in the Glagolitic alphabet about 1400 (held in the Municipal Library in Tours). He wanted to show his renowned colleagues of Sorbonne that except Hebrew, Greek and Latin also existed a genuine Croatian alphabet, or alphabetum chrawaticum as he called it, having a great graphic and lexical value. In 1401 he defended his doctorate in theology. In 1403 his name was included in the big scroll of professors of the University of Paris. Since 1404 he was also a canonist-penitentiary in Tours, in the nun's convent Beaumont, until the end of his life. With his book "Le chasteau de virginite", written in Latin and French in 1411, he entered the history of French and European literature. There exist many of its copies from the 15th century, plus three French printed editions (1505, 1506, 1510) and one Latin (1726), thus proving its popularity in Europe. His manuscripts, some of them written in the Croatian Glagolitic, are held in the City Library (former Cathedral Library) in Tours. He was also very fond of Istria, to which he referred as a part of his Croatian homeland: Istria eadem patria Chrawati. Photos of some of his manuscripts can be seen at Juraj Slovinac (in Croatian). One of his original manuscripts is held at Yale University Library.
"Tractatus de Ecclesia", written by Ivan Stojkovic de Corvatia (or Iohannes de Carvatia, also known as Jean de Raguse, 1390/95-1443), a professor at the University of Paris, was the first systematic tractate about the Church in the history of Catholic theology. Ivan Stojkovic also headed the delegation of the Council of Basel to Constantinople, aiming to negotiate the Ecumenical questions of the Eastern and Western Church. He wrote that he was from Dubrovnik, which was a Croatian city (de Ragusio quae civitas est in Charvatia).
In the 15th century Luka Pozezanin and Juraj from Cazma were lecturing on mathematics at the University of Vienna. At the same institution Valent from Koprivnica was lecturing on natural philosophy, Ladislav from Pozega was lecturing on astronomy, etc.
Croatian Latinists
Juraj Sizgoric (~1420-1501) was born in Sibenik, and studied in Padova, where he became doctor of sciences. He published a collection of verses "Ellegiarum et carminum libri tres" in Venice in 1477, which is thus one of Croatian incunabula. His book bears witness of a very rich spiritual life in Dalmatia in the 15th century. He also described tragic events related to spreading of the Turkish Ottoman Empire.

Konrad von
Grünberger: Sibenik in
1486
Among Croatian Latinists and writers in Croatian a central place is occupied by Marko Marulic, who is the "father of Croatian literature" (born in Split, 1450-1524). He was the most famous spiritual writer of his time in Europe, and also the first who defined and used the notion of psychology, which is today in current use.
His book De institutione bene vivendi (six volumes, 64 chapters), published in Venice in 1506, had fifteen editions until 1686 and was translated from Latin into
- Italian
- German (five editions between 1583 and 1614, all in Köln, in parts already in 1568)
- French (7 editions, the first one in 1585)
- Flemish
- Japanese (in Nagasaki, in parts, 1585)
- Portuguese and
- Czech,
altogether 40 editions. It is well known that St. Francis Xaver had taken only two books on his long pilgrimage to the East (India, Japan and China): the Bible and De institutione. Furthermore, in his testament St. Francis Xaver asked that Marulic's book be buried with him. Therefore we may conclude that Marulic was a spiritual father of St. Francis Xaver. St. Francis Xaver's personal sample of Marulic's book was kept in Madrid in a collection of valuables until 1937, when it had dissapeared. St. Ignazio Loyola included De Insitutione into the list of basic references for the formation of Jesuits. Both St. Francis Xaver and St. Ignazio Loyola were Basques.
Marulic left us many beautiful verses and the epic poem Judita (Judith) written in the Croatian language, for which he says expressly to be written in the Croatian verses (versi harvatski). Some of his original verses are held in Glasgow (GB). His Judith was translated into English, Hungarian, French, Italian, and some parts into Spanish. Marulic translated from Latin into Croatian the famous "De imitatione Christi" by Thoma de Kempis.
From the verses of his epic poem Judita, it can be see that Marko
Marulic was familiar with Croatian
Glagolitic Script and with Glagolitic Church-Slavonic literature
(see [Hamm,
p. 166]: "...vidjeli smo da je morao poznavati glagoljicu i glagoljska
crkvenoslavenska djela..."). Each line of the poem is written as a
doubly-rhymed dodecasyllable (i.e., each line has 12 syllables), which
is extremely difficult to compose.

The title page of Marko Marulić's book Judita, written in 1501,
printed in Croatian language in Venice 1521. Source of the photo Wikipedia.
Transcription:
Libar Marka Marula Splićanina v kom se
uzdarži historija svete udovice Judite u versih
harvatski složena kako ona ubi voj-
vodu Oloferna posridu voj-
ske njegove. I oslobodi pu-
k israelski od veli-
ke pogibli.
+
Please note:
u versih harvatski = in Croatian verses
The original Marulic's manuscript of "De institutione bene vivendi" has been stolen from the Croatian National Library in Zagreb around 1980. Any information about this would be appreciated.
According to investigations of a French specialist Charles Béné, Marulic's texts have been used extensively by Thomas More and Henry VIII. It is known that Marulic's "Evangelistarium" that was read by Henry VIII bears many comments by the King. It is considered that two of the king's three literary works were written under the influence of Marko Marulic. Charles Béné has translated Marulic' Judita from Croatian into French (La Judith).
A page of Marulic's Evangelistarium
annotated personnaly by the English King
Henry VIII, kept in the British Library (843 K 13), see Charles
Béné:
La reception des oeuvres
de Marulic dans les provinces du Nord
,
in Colloquia Marvliana IIII, Knjizveni krug, Split 1994., p. 51

Marko
Marulic's Evangelistarium
published in Spanish in Madrid in 1655. Note Croatian
Coat of Arms in the middle.
Photo exhibited by The
Split Literary
Circle.
Marulic's poem "Carmen de Doctrina Domini Nostri Jesu Christi pendentis in cruce" was translated into English as "A Dialogue betwext a Christian and Christ hanging on the Crosse" by St Philip Howard, Earl of Arundel (1557-1595).
According to C. Verdiani, Marulic is also the author of the Florence Codex, which contains a biography of St Jerome written in the Croatian language. There he wrote
and a brilliant crown of the Croatian language.
In Croatian: Jerolim je nass Dalmatin, on je dika, posstenje i slava i svitla kruna hrvatskoga jezika.
Marulic's verses appeared printed in the Glagolitic Script alreday during his lifetime, in Transit of St Jerome (Transit sv. Jerolima), published in the town of Senj in 1508 under the title of Anjelske kriposti, in 144 doubly-rhymed dodecasylabic (ie 12 syllabic) lines. These verses, transcribed into the Glagolitic from the original Croatian text in Latin script, can be found by the end of the book. Many thanks to academician Anica Nazor for this information (2007). Here is a part of describing wisdom of St Jerome, see [Bratulic, Il poeta Marco Marulic e la tradizione glagolitica in Croazia, p 232]:
| Bog
razum skupi u njem tr izvrstnu
mudrost, Sveta Pisma po njem da prosine svitlost, Prorokov otajna, Kristove pritaci Nam su sad nahajna, jer je on stlmaci. Vsu knjigu latinsku i grcku umise I osce ijudejsku… |
Older Croatian Glagolitic Transits of St Jerome have been studied by [Stefanic].
Marko Marulic sent a dramatic letter to the Pope Hadrian VI, describing an extremely tragic position of the Croats threatened by the onslaughts of the Ottoman Empire and asking for help.
Jean Garret (Ioan Garetij) of Louvain, in his writing De era praesentia corporis Christi in sacrmaneto Eucharistiae, 1561, cites Marko Marulic
His books were known not only in the whole of Europe, but also in Japan (in the 16th century) and South America. For example, parts of De institutione bene vivendi were translated into Japanese already in 1585, published in parts in Nagasaki under the title Sanctos no gosayuno, see Franolic (he mentions 1595 instead of 1585).
More than 500 copies of Marulic's books are kept in Germany (60 libraries), from Franz Leschinkol: Povijesna uloga Evandjelistara i Institucije u 16. stoljecu, in Colloquia Marvliana IIII, Knjizveni krug, Split 1994., pp. 90 and 193
Alonso de Villegas, Spanish author of a famous book Fructus Sanctorum (printed in Paris in 1624), refers to Marulic's De Institutione on almost every page. Another Spanish Christian humanist, Juan Lorenzo Palmierno (Laurentius Palmyrenus), in four of his texts published between 1564 and 1578 mentions expressly to be inspired by Marulic's books. Moreover, in one of his dramas there is a figure called "Marulus". And Professor Michael Neralich (lecturing Spanish and comparative literature at the University of Clermond-Ferrand) considers that the figure of "Andrea Marulo" in the novel Trabajos de Persiles y Sigismunda by Cervantes is inspired by Marulic. There is no doubt that Cervantes was familiar with Marulic's books, since they were translated into Spanish by Fernandez de Ruenga. In the Library of Cristoph Columbo in Sevilla, founded by Hernando Colon (son of Cristoph Columbo), there are many books by Marko Marulic, and even his "Judita" written in Croatian!

Sanctos
nogosagveono,
1591, written in Japanese language and in Latin script, contains
Marulic's texts; see Franz Leschinkol: Povijesna
uloga
Evandjelistara i Institucije u 16. stoljecu,
in Colloquia
Marvliana IIII, Knjizveni krug, Split 1994., pp. 98
One of Marulic's
tractates has been translated into Icelandic
in 1601.
According to dr. Bratislav Lučin (see here,
p. 26), twelve editions of Marulić's books were published during his
lifetime - in Latin and Croatian. In the last 500 years (up to 2024),
his texts were republished considerably more than five hundred times,
in as many as fifty countries througout Europe, from Portugal to
Czechia and from Italy to England, and even a few editions were
published across the ocean. He was translated into 15 languages:
Some of Marulić's hitherto unknown works were discovered (in the period
of 1995-2024):
- Latin epigrams, kept in Glasgow
- The life of St. Jerome, kept in London
- his letters written in Italian and Latin, kept in Venice
- commentaries of Catulllus' poems, kept in Paris,
- numerous writings, and among them are especially important his autographs.
The literary center Marulianum,
established in 1995 in the city of Split, has published numerous
writings by Marulić (by establishing Colloquie Maruliana journal),
monographs and scholarly studies, organized scientific meetings. This
all has enabled establishing a new branch of Croatistic studes - Marulology.
Marko Marulic was writing in Latin and Croatian, and was
translating from Latin into Croatian, from Croatian into Latin, from
Italian into Croatian, and even from Italian into Latin (the first
singing of Dante's Inferno (i.e., Hell), and Petrarca's canzona Vergine bella). See [Pšihistal 2024, p. 259].
When St. Francis Xaver arrived to Kogoshima in Japan in 1549, he also brought Marulic's "De insitutione bene vivendi". According to bishop Hamao from Yokohama, president of Japanese Bishop's Conference and of Asian Caritas, the formation of earliest Japanese Christians had been very probably based on the spirituality of Marulic. See here (in Croatian). It is interesting that in Berlin a monument of Marko Marulic was set up in 2000. In the Library of Congress, Washington, a symposium was held devoted to his work.
- Marko Marulic, Humanist from Split
- Marko Marulic - Marcvs Marvlvs (in French), by Mirko Tomasovic, translated from Italian by Charles Béné
- MARVLIANVM, Centar za proucavanje Marka Marulica i njegova humanistickoga kruga, Split
- Marko Marulic: De insittutione bene vivendi (scrollable book), National and University Library, Zagreb
- Marko Marulic: Judita (scrollable book), National and University Library, Zagreb
- Epistola domini Marci Maruli Spalatensis ad Adrianum VI. Pont. Max. (scrollable book), National and University Library, Zagreb
- Colloquia Maruliana
- Bratislav Lučin (ed.): The Marulic Reader, Knjizevni krug Split Marulianum, Croatian World Congress, Split 2007., ISBN 978-953-163-284-3
- Bratislav Lučin: Marko Marulic 1450-1524, Zebra plus, Split 2008., ISBN 978-953-96566-4-3, in Croatian and German
- Zvonko Pandžić: Nepoznata
proza Marka Marulića,
Tusculanae editiones, Zagreb 2009., ISBN:
978-953-95144-6-2; (the monograph is described by Stjepan Krasić: K
rješenju marulićevskog pitanja [PDF],
Filologija 54, Zagreb 2010.)
- Mirko Tomasović: Nove
slike iz povijesti hrvatske književnosti, Matica hrvatska,
Zagreb 2008.
- Mirko Tomasović: Raspre i rasprave, Matica hrvatska, Zagreb 2012.
- Ružica Pšihistal: Kršćanski humanist i prvi klasik hrvatske književnosti, Obnovljeni Život, Vol. 79 br. 3, str. 257-260.
De institutione bene vivendi per exmpla sanctorum
2. The third Latin edition printed in Koeln in 1530
3. The third Italian edition printed in Vencie in 1597, translated from Latin by Remigi Nannini
Evangelistarium
5. The first Italian edition printed in Florence, translated from Latin by Silvano Razzi
Quinquaginta parabolae
Regum Dalmatiae et Croatiae gesta
Marko Marulic: Animadversio in eos qui beatum Hieronymum Italum esse contendunt
Regum Dalmatiae et Croatiae gesta is Marko Marulić's free translation in Latin of the Croatian Chronicle, i.e., of the Croatian redaction of the Ljetopis popa Dukljanina, printed in 1510. The Croatian redaction of the chronicle, written in Croatian Script (Croatian Glagolitic or Croatian Cyrillic Script?) was discovered by a Split nobelman Dmine Papalić in Krajin, in the house of Marković in Poljica. Upon his request, Marulić trenslated the text into Latin in 1510 and dedicated to him.
This text was first printed in 1666 in Amsterdam, as a part of the monograph De regno Dalmatiae et Croatiae prepared by Croatian historian Ivan Lučić (Ioannes Lucius) of Trogir (1604-1609).
Marko Marulić was the author of his famous poem Molitva suprotiva Turkom (Prayer Against the Turks), that he wrote in Croatian language:



Only God can libearte us from our enimies the Turks, by its infinite power.
*This acro-verse was discovered by Luko Paljetak, a Fellow of the Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts
(published in 1979)
Lit. Vedran Gligo (ed.): Govori protiv Turaka / Orationes contra Turcas, (summaries: [PDF, Raukar], [PDF, Mijatović], [PDF, Nazor), Logos, Split 1983., 650 pp., with facsimiles
The court of the king Mathias Korvin was a strong European humanistic center, to which the Croats gave a deep imprint. Thus the tutor of Mathias Korvin was Ivan Vitez (1405-1472), a Croatian Latinist, who also had the merit to open the University of Bratislava (capital of Slovakia) and the Academy and library of Budim (part of today's Budapest). He was a cardinal and occupied the position of the king's chancellor. In his speech in Vienna he asked for help to stop the penetration of the Turkish Ottoman Empire to Croatian lands.
Jannus Pannonius (1431-1472), a Latin poet and humanist at the court of Mathias Korvin and a Croatian ban (viceroy), was famous in his time. He was born in a small village near Aljmas on the river Danube (the area that during the Serbian aggression in 1991/92 suffered indescribable atrocities) and died in Medvedgrad near Zagreb.
Antun Vrancic (lat Antonius Verantius, hungarized name Antal Verancsics, born in Sibenik in 1504) studied in Padova, Vienna and Krakow. After spending almost 20 years as a secretary and diplomat at the court of Ivan Zapolja, he continued his career at the court of Ferdinand I Habsburg in 1549. As the king's envoy he had a delicate task to negotiate with the Turks (he spent altogether 6 years as a diplomat in Turkey). Together with a Flamish diplomat Busbeck he discovered the Ankara plate (Monumentum ancyranum, held in the National Museum in Vienna), which is quite important for understanding the history of the Roman Empire, especially during the time of the Emperor Augustus. As a diplomat he travelled to France, Italy, Poland, England (on a diplomatic mission to the court of King Henry VIII), Turkey etc., and was exchanging letters with Erasmus of Rotterdam. In Krakow, Poland, he published two collections of poetry in the Latin language ("Elagiae" and "Otia").

Portrait
of Antun Vrancic by
outstanding
Croatian
painter
Martin
Rota Kolunic from Sibenik

Antun Vrancic, that is, Antal Verancsics, is in Hungarian literature usually described as Hungarian, which is no surprise. The same for Faustus Verancsics, his very famous relative.
It is little known that the famous Venetian painter Tizian portrayed Frane Vrancic - father of Antun Vrancic.
One of the oldest secular dramas in Europe is `The Slave', written by Hanibal Lucic (born in Hvar, 1485-1553), a Croatian writer. In 1612 a municipal theatre in Hvar (on the island Hvar) was built up. It was the first communal theatre in Europe (i.e. the first theatre in a closed building).
Croatian language was taught in all church Universities in the 17th century as one of six world languages:
- Latin,
- Greek,
- Hebrew,
- Arabian,
- Caldean (Aramaic),
- Illyric (Croatian).
- University of Bologna,
- University of Padova,
- University of Vienna,
- University of Ingolstadt,
- University of Köln,
- University of Louvain,
- University of Paris,
- University of Toulouse,
- University of Salamanca,
- University of Madrid (Alcalŕ de Henares).
This hitherto completeley unknown fact has been published in a monograph by academician Stjepan Krasic, Pape i hrvatski knjizevni jezik u XVII. stoljecu, Zagreb - Citluk, Matica hrvatska, 2004. (Academician Krasic is professor of history at Papal University of St. Thomas Aquinas in Rome). See an interview with Stjepan Krasic at www.glas-koncila.hr. Stjepan Krasic also discovered that the University of Zadar, i.e. Universitas Jadertina, was founded in 1396, see here.
One of the well known Latinists was Rajmund Kunic (1719-1794), who translated the Iliade from Greek into Latin in 1776 (the first edition in Rome, second edition in Venice in 1784). His translation is even today generally regarded as the best one in the world. Kunic was a member of the Accademia dell'Arcadia in Rome.
Benedikt Stay-Stojkovic (1714-1801) was a famous Latin poet, a member of Accademia dell'Arcadia. He studied in Dubrovnik and Rome, and was a professor at Sapienza. He wrote two extensive epics:
- "Philosophiae versibus traditiae libri VI" (Six books of versified philosophy), published in Venice in 1744. It contains 10,249 hexameters, in which he presented Descart's philosophy. Second enlarged ed. was published in Rome, comprising 11,229 hexameters.
- "Philosophiae recentioris...versibus traditiae libri X", was devoted to Newton's scientific and philosophical views, published in 1755. It contains as many as 24,227 hexameters. Commentaries and notes have been written by an outstanding Croatian Latinist and scientist Rugjer Boskovic.
One of the most outstanding Croatian scientists in history was Rugjer Boskovic (1711-1787), also brilliant Latinist poet. He wrote an extensive scientific poem De solis et lunae defectibus (On Solar and Lunar Eclipse), published in London in 1760. It contains 5570 Latin verses, and was dedicated to the Royal Society of England whose member he was. In the title one can read "Father R. Boskovic, of the Jesuit Order", although at that time it was forbidden for Jesuits to live and work in England. The epic was written in the manner of Roman classics, in dactilus hexameter.
For more information see Latin as literary language among the Croats
The oldest known Croatian book in the Latin script was "The Order and Law", written in 1345 by the Dominicans from Zadar.
Brne Zamanja (Bernardus Zamagne, 1735-1820) was born in Dubrovnik. He lectured rhethoric in Rome, Livorno, Siena, and Greek language and literature in Milano. His translations into Latin comprise Greek classics and Croatian authors (Gundulic) and Croatian folk poetry.
For more information see
Croatian Humanists
Pavao Dalmatin was lecturing canonical law at the University of Bologna. His book "Summa poenitentia" (1220) had been rewritten in as many as fifty copies in the period between the 13th and 15th century, that are now held in many European libraries. It also had three printed editions in the 18th, 19th and even in the 20th century. This book represents the first known manual of moral theology for confessionals. Pavao Dalmatin was a collaborator and a good friend to St. Dominic.One of the most important Croatian humanists in the 15th century was bishop Nikola Modruski, the creator of the first known Latin incunabula written by a Croat author ("Oratio in funere Petri Cardinalis S. Sixty," 1474, Rome). At the same time he was a great promoter of the Croatian Glagolitic Script. He was also the papal nuncio at the court of the Bosnian ban (viceroy) Stjepan Tomasevic and at the court of king Mathias Corvin in Budim. His huge library, whose origin is from Modrus, was left to the Vatican. He wrote a treatise in defence of the Glagolitic Script in Modrus Diocese. It is regarded to be the first polemic treatise in the history of Croatian literature. It is interesting that Nikola Modruski was born in Boka kotorska. In 1474 he printed the first book among the Croats, in the Latin language. For additional information see here.
A Croatian Dominican priest Beniamin was editor in chief of the first Russian Bible (finished in 1499) written in Russian Church Slavonic. It was the first Bible also among all Orthodox Christian Slavs. It served as a basis of later printed Russian editions in 1580-81 and 1663, which had spread among Orthodox Christian Slavs. Beniamin's original translations of the Vulgata are even today left unchanged in many parts of the contemporary Russian Bible. It is interesting that the old Russian Bible has many Croatian characteristics in phonetics, morphology and vocabulary, for example,
- kovac (blacksmith)
- loviti (to hunt)
- plijen (prey)
- staja (stable)
- stijena (rock)
- nastojati (to strive)
- puk (common people)
- obitelj (family)
- and even - gusterna (stone water cistern)!
According to the famous
Russian church historian Makarij,
Beniamin was the chief personality in the creation of Genadij's Bible.
This undertaking was of great importance for the Russian Church, in
particular for the development of Russian spiritual literature.
Beniamin also translated the 8th part of the latest 1486 Strasbourg
edition of the famous work Rationale
divinorum officiorum of
Guilelemus Durandus - Spectator, which was devoted to calendar
calculations and astronomy. In this way Beniamin influenced also the
development of Russian astronomical terminology, in particular -
Russian names for star constellations. According to Vladimir
Rozov (Russian emigrant in
Zagreb), Beniamin (or Venjamin
as he is called in the Russian literature) represents the
earliest
humanist on the Russian soil,
and furthermore, Beniamin was
actually editor in chief
of the first complete Church-Slavonic
Bible among Pravoslav Slavs. Beniamin also had important role in
opening new schools in Novgorod (until that time there were no real
schools in Russia). The name of Croatian Dominican Beniamin is
completely unknown among Croats in time when these lines are written
(1999), except to several specialists. The Croats can be rightfully
proud of this little known person for his great Ecumenical role.
Beniamin's mission in Russia represents an important and almost
forgotten bridge between Catholic and Orthodox Christianity.
Literature:
Vladimir Alekseevic Rozov
(1876-1940), born in Kyiv, capital of
Ukraine, in the family of professor of the Kyiv Spiritual Academy. In
1903 graduated from the Kyiv University (Faculty of Philosophy). In
1907-1908 investigated the Slavic manuscripts on the Near East.
Professor of Slavic philology in the Nizyn Institute (1916) in Ukraine.
Professor at the University of Tavrid (1918-1920; Tavrid is today's
Herson in Ukraine). Lectured Russian language at the University
of Zagreb (1920-1940), and
died in Zagreb. Literary critic,
culturologist, publicist, investigator of Russian-Croatian relations,
author of many articles. [more].
Many thanks to Mr. Oleh Hirnyk, Lviv, Ukraine, for kind help.
Andrija Jamometic, a descendant of noble family from the town of Nin on Croatian littoral, was born in 1420-30, and died around 1486. He obtained excellent education in Padova, and later became outstanding diplomat in the service of Pope Sixto IV, tsar Friedrich III, and free cities like Nürnberg. In the Dominican convent in Udine (Italy) there was his portrait (now lost), with the following inscription: Brother Andrija, Croat, member of Udinese convent, famous for his knowledge of theological science and connoisseur of foreign languages. Pope Sixto IV apppointed him Archbishop of Granea in Greece. He was deeply involved in Ecumenical questions related to delicate relations between Eastern and Western Christianity. He also insisted on the necessity to save Constantinople and Eastern Europe from Turkish onslaughts. In his letter written in 1482 to many European rulers, Jamometic sent an appeal to organize the Third General Church Council to discuss Ecumenical questions, and to continue the unfinished Basel Council. He also sent an appeal to many universities, for example, to theological faculties in Vienna, Paris, Köln, Louvain, Krakow, and other similar institutions throughout Europe. His tragic destiny was similar to that of Thomas More about 50 years later.
Juraj Dragisic (Georgius Benignus, 1445? - 1520) was a Croat born in Srebrenica in eastern Bosnia (known by the Greater Serbian slaughter of Muslim Slavs in 1995 that the international community watched with fingers crossed, though it had been "UN protected area"). As a young Franciscan, when Bosnia fell in the Turkish hands in 1463, he escaped across Zadar to Italy. Due to the generous support from several Italian noble families he obtained excellent university education in Rome, Bologna, Florence, Padova, Ferrara, Paris and Oxford. His career started on several Italian universities, where he was lecturing philosophy and theology (including Sapienza in Rome). At the same time he was an educator and tutor of the children of the Toscan Archduke Lorenzo Medici - one of his children became a Pope (Leon X). By the end of the 15th century, after 30 years spent in Italy, he continued his career in Dubrovnik. Juraj Dragisic was in touch with the most outstanding names of the European Humanism of that time, and is the author of several books in the Latin language: "De natura celestium spiritum", Florence, 1499, "De natura angelica", Dubrovnik, 1498. He also spent some time as an envoy of the Pope at the court of Emperer Maximillian in Innsbruck. In 1514 he proposed the reform of the Julian calendar, which later became known as the Gregorian calendar.

In 1515 a question was raised by a German theologist on the admissibility of Talmud within the Christian doctrine. As a representative of the theological commission in charge to express his opinion, Dragisic was resolutely for acceptance of Talmud. Being accused by a Great Inquisitor of Germany for heresy, he was defended by the famous Erasmus of Rotterdam. See [Gregory Peroche], p. 65.
The last book by Dragisic entitled "New and Old Rules of the
Dialectical Art" (Artis
dialecticae praecepta vetera et nova, 1520), dedicated to the
questions of Logic, has been prepared in Dubrovnik and published in
Rome. Croatian Logic Association has founded the Juraj
Dragišić / Georgius Benignus Prize in Logic.
This very interesting Bosnian Croat, and outstanding European intellectual of his time, is treated in a monograph written by Croatian scientist Mirjana Urban: Juraj Dragisic, published in Dubrovnik in 1998. We learn that Dragisic wrote 7 printed book (out of them 5 incunabula, including one very beautiful in Dubrovnik), 12 handwritten books, and at least 4 lost books.
Croatian Latinity also includes the Latinity of Bosnian
Franciscans. See e.g.,
- Stjepan Pavić (ed.): Latinske pjesme bosanskih franjevaca, Synopsis, Sarajevo - Zagreb 2015.
We find it pertinent to add that the monograph of Mirjana Urban is dedicated to her son Pavo Urban, a young Croatian photographer and cameraman, killed in 1991 during Serbain attacks on the city of Dubrovnik. He had the same profession, and the same tragic destiny as Gordan Lederer.
The reader will not mind a short digression with a word or two about Srebrenica, where Juraj Dragisic was born. Before the Ottoman penetration to Bosnia, which started in the 15th century, its population was mostly Croatian. In 1600 it had about 200 Catholic houses. Srebrenica was a part of the Bosnia Argentum Archdiocese held by the Bosnian Franciscans. Its Catholic church from the 14th century had not been destroyed by the Turks, only its bell-tower was rebuilt to a minaret, so that the former church served as a mosque, even till these days (i.e. for more than 500 years). The author of these lines visited it in 1981, when the population of Srebrenica had a large Muslim majority. As a "UN protected" zone, this city, overpopulated by tens of thousands of exiles (mostly Muslim Slavs), was a victim of the Greater-Serbian ethnical cleansing and genocide in July 1995. The fate of about 8,000 people is not known. The Catholic church - mosque was destroyed.
Thomas Illyricus (Vrana near the city of Zadar 1484 - 1509 or 1501) was especially well known in France, due to his sermons that ordinary people liked very much. Known for his unusually long sermons, he spent the longest period of his life in the province of Occitania, but also in Italy and in Spain. In 1518 Father Thomas arrived to Toulouse, upon the invitation of its citizens. He was also in Villefranche-la-Rouergue (known for the Croatian Rebellion against the Nazis in that city in 1943), in Bordeaux, Geneve, Grenoble, Aix-en-Provence, travelling from city to city and from village to village. He was also preaching in Lyon. The city of Arachon, in which Father Thomas founded the Basilica of Notre Dame, today has a street called rue Thomas Illyricus in his honor. His name also appears in various sources in the form of Thoma Illirico and Thomas Illyric.
Here are two interesting citations (for those who can read French):
- « Mais peut-ętre que, frappé de la nouveauté de ce point de
vue, l'un de vous me dira : « Frčre Thomas, pourquoi t'es-tu donc
consacré ŕ la solitude ? Pourquoi ces bois retirés te plaisent-ils ? »
Je lui réponds : « Une ville est pour moi une prison, la solitude un
paradis. Je trouve d'ailleurs tant de difficultés partout oů je suis
qu'en face de ce lieu inhospitalier lui-męme je suis contraint de crier
bien haut par écrit et en public. »
- « Il est dit : « Demeure en paix. » Tu ne peux tout ŕ fait
craindre un homme d'Illyrie qui se cache dans des cavernes retirées, en
compagnie des bętes. Je tends mes filets autour des villes, diras-tu,
je séduis le peuple, j'apporte le schisme. Mais jamais je n'ai fait
cela et jamais je ne le ferai, que crains-tu donc ? »
Lit. [Christophe
Dolbeau, pp. 27-26]
Simun Kozicic Zadranin (or Benja), the bishop of Modrus, was a humanist, Glagolitic writer and Glagolitic typographer with his printing house in the city of Rijeka. He is known for his speech about the insupportable pressure of the Ottoman Empire on Croatia to the participants of the Lateran Council in 1513. The same purpose had his speech De Corvatiae desolatione (On Devastated Croatia) held in the presence of the Pope Leon X in 1516. For additional information see here.

1516 speech of Simun Kozicic Zadranin, Bishop of Modrus: De Coruatiae desolatione
(On
Devastated Croatia), published in Latin original in Paris, France, 1517
It is interesting that Kozicic's 1516 speech, held in Latin, has been translated into French already in 1518, published again in 1560 and 1561, all three times in Paris. In the French translation the author of the speech is described as "reuerend pere en Dieu leuesque de Modrusie, ambassadeur deuers sa Sainctete pour le pais de Coruacia" (reverend father in God from Modrus, emissary in front of His Holiness from the country of Croatia). It is interesting that his Kožičić's Latin words pauperes illi nostri are translated as "noz poures gentz de Coruatie" (our poor people of Croatia).
Bratislav Lučin: Kožičić na francuskom - 1518. godine!
Toma Niger (Toma Nigris, bishop of Skradin and later bishop of Trogir) as an emissary of Ban Petar Berislavic, was on a diplomatic mission to the Roman Pope and to the Emperor Charles the Fifth in Brussels in 1520, to appeal for help to the defence of Croatia against the Turks. The same year the Croatian Ban was killed in the battle against the Turkish army at the town of Korenica.

Prince Bernardin Frankapan, born and educated in the Glagolitic environment, was an important promoter of the Croatian Glagolitic literature. He founded the Glagolitic scriptorium for translating the Bible in the town of Ozalj. In his speech Oratio pro Croatia held in Nürenberg in 1522 he sent a dramatic appeal to the German State Council and to Europe to help the Croats in their struggle against the attacks of the Ottoman Empire. Simun Kozicic Zadranin wrote for him that "even under arms and with sword, all the time he writes and translates". For additional information see here.
Sigismun Gelenius (1477-1554), a Czech humanist, is the author of a Latin Czech dictionary Lexicon Simphonium published in Basle in 1537, where one can encounter Croatian words as well (in particular in its second edition from 1547; information by Mr. Ivan Dubravcic, Delft, The Netherlands).
One of the greatest promoters of Protestantism in Europe was Flacius Illyricus (Matija Vlacic, born in Labin in Istria, 1520-1575). As a young Croatian philosopher, at the age of 24 he was appointed to be a professor of Hebrew and Greek at the University of Wittenberg, the center of Protestantism. The bibliography of his work is enormous - three hundred books and brochures. His "Catalogus testium veritatis" (Magdeburg, 1555) represents a tremendous historical documentation, probably the best polemical book of his time. French edition appeared in Strasbourg in 1526 and in Lyon in 1597. His pamphlet "Contre la principauté de l'évęque de Rome" was printed in Lyon in 1563. He wrote also about Croatian churches that ever since had liturgy in the Croatian version of the Old Church Slavonic language, using holly books written in the Croatian Glagolitic Alphabet. He was the organizer, editor in chief and the chief writer of the famous "Ecclesiastica historia" (The History of the Church), that appeared in 13 volumes in Basel.
Flacius Illyricus: Clavis
Scriptuare Sacrae, Regensburg, 1567
(from the 2006 exhbition
in
NSK, Zagreb)
His greatest linguistic work is "Clavis Scripturae Sacrae" (The key to the Sacred Script, it contains about 7.5 million characters), Regensburg, 1567, analyzing lexicographically the content of the Old and New Testament. He is considered to be the founder of hermeneutic philosophy. When writing about Istria (peninsula in the Adriatic), he calls it `the sweetest homeland'.
There is a work of a famous French polyhistor Guillaume Postel, with the preface written by Flacius Ilyricus (Matija Vlacic):
Postel Guillaume: Epistola Guilemi Postelli ad C. Schwenkfeldium, cum prefacione m. Mathiae Flacci Illyrici, Jenae, 1556. (see [Marianna D. Birnbaum, p. 510])
It is interesting that Guillaume Postel presented Croatian Glagolitic Scritp in one of his books, calling it Alphabetum Hieronymianum seu Dalmaticum, aut Illiricum.
A Croatian Jesuit Mark Antun de Dominis (born as Marko Domnianich on the island of Rab, 1560-1624) ranked among the greatest European philosophers and scientist of his time. His career of a university professor started in Padova. He was especially esteemed in England, where he was invited by king James I. There he lived at the Court of the Archbishop of Canterbury and was appointed to be the Windsor Dean and the king's chancellor.

Dominis arrived to London in December 1616 with a great pomp after his apostasy from Rome. Four days after the spectacular welcome, Dominis was placed fifth place next to King James. This meant, according to the protocol of the time, that he was fifth in the hierarchy of the state. In 1617 he was lecturing in Cambridge and Oxford. In Cambridge he was awarded the title of doctor of divinity. His sermons in London were printed in Italian, English and Latin. His book "The Ecclesiastical State" was printed in Latin in England, with permission of the King.
It is interesting that Dominis introduced the word "puritan" into English in its modern meaning, which was earlier used only in theological literature and had a very narrow meaning.
His work in physics was cited in I. Newton's book "The optics" published in 1704 (page 147). Among other things he contributed to the explanation of the phenomenon of the double rainbow. His theory of tides was based on the idea of attractive force between the Moon and the Earth, which was later made precise in Newton's theory of gravitation. He also discovered the phenomenon of diffraction of white light (see G. Hund's "Geschite der Physik"). However, his main preoccupation was the problem of European peace and the reform of the Church. In 1618 his work "The Rocks of Christian Shipwrecke" was printed first in Italian, and then in English. It was held an important apologetic work of Protestant theology, and was soon translated into French. It was read throughout Europe.
After six years of stay in England his relation with the Anglican Church and the King himself cooled down, though he had given the Anglican Church one of the most important doctrinal weapons (for more details see [Mardesic], p. 162).
His work "De Republica
Ecclesiastica", which was published in
ten books in London, brought him the anathema of Rome. He was
imprisoned by Inquisition and when he died, the burial of his body was
not allowed. It was burnt, together with his manuscripts, on the square
of Campo dei Fiori in Rome, where Giordano Bruno had been burnt twenty
four years earlier.
Branko
Franolic: Two Croatian refugees at St.
James’s Court at
the beginning of the 17th century
A
Croatian theologist, ecumenist,
panslavist and musicologist Juraj
Krizanic (1618-1683) was
trying to initiate the dialog on the unification of the Russian Church
with Rome. He dreamed about an open and peaceful dialog with Orthodox
Christians. His major works are "Razgovory ob vladatelstvu" or
"Politika" (written in panslavic Esperanto that he
invented as a combination of his native Croatian, Russian and
church-slavonic), written during
his 15 year exile to Siberia and the panslavic grammatical book
"Gramatično iskazanie ob ruskom jaziku" (Tobolsk, 1665). He also spent
some time in Ukraine, where he had close ties
with some of leading scholars. Krizanic wrote "Historia de Siberia" in
1680, with dedication to Jan Sobiesky. It is known that during his
sojourn in Rome he supervised a publication of musical works of the
Portuguese king D. Joăo IV. According to Krizanic's
systematization of science, music should be regarded as a part of
mathematics. He wrote his "Asserta musicalia nova" in 1650. Krizanic
died near Vienna while participating in its defence against the Turks
in the Ukrainian troops that adjoined the troops of the Polish king Jan
Sobiesky.
According to a Russian
historian S.M. Solovev (see his Istorija
Rosii s drevnejshih vremen,
vol. XIII, Sanktpeterburg 1868),
Krizanic's book Razgovory ob
vladatel'stve
(Discussion about
Governement) served as a handbook to Peter the Great, founder of the
modern Russian state. Russian scholars consider Juraj Krizanic as the
father of the Slavic comparative philology as a scientific discipline.
- Ivan Golub: Simpozij o Jurju Krizanicu u Moskvi [PDF], 2005, Russia
- Ivan Golub: Juraj Krizanic, teolog pomirenja [PDF], 1984, USA
Vinko Paletin (1508-cc 1575), born on
the
island of Korčula in Croatia, was Croatian cartographer, writer,
diplomat and Dominican priest. In 1530 he went to Yucatán, and in 1546
he completed his studies of theology in Bologna. He was a professor of
Mathematics in Vicenza and at a diplomatic mission at the court of the
Spanish king Philip II. In 1551, Paletin completed a detailed map of
Spain. In 1554, he translated from Spanish into Italian the book by
Pedro Medina: L’arte del navigar
(The Art of Navigating).
- Incipit prohemium in tractatum de jure et justitia belli, quod habent reges Castellae et Legionis in regionibus occidentalis Indiae, quam quidam novum apellant orbem, ad Serenissimum Caesarem ac potentissimum Regem Philipum, Regem Hispaniae, Angliae etc. editum per Reverendum Patrem Fratrem Vincentium Paletinum Corzulensem, natione Dalmatam, ordinis Sancti Dominici et sacrae theologiae baccalaureum, kraćeg naslova De Jure et Justitia belli contra Indos ad Philip(pum) II. Hisp(aniae) Regem
It was translated into Croatian in 1994. (Vinko Paletin: Rasprava o pravu i opravdanosti rata,
Zagreb 1994., translated by Franjo Šanjek and Mirjana Polić Bobić).
According to the studies of a Spanish Dominican Isacio Pérez
Fernández (1922-2003), published in his monograph Nombre, vida y adventuras del conquistador
anonimo Vinko Paletin de Korcula, Vinko Paletin is the author of
the following book:
- La Relacion de la Nueva
Espańa
A Croatian Jesuit Nikola Plantic (born in Zagreb, 1720-1777) studied in Zagreb, Graz, Vienna and Trnava in Slovakia. He was teaching logic and philosophy at the Jesuit University in Cordoba in Argentina.
In some books we can read that Plantic
allegedly had an important role in the formation of the unique Jesuit
Kingdom in Paraguay, established
for the wellbeing of native Guarani
Indians.
It is true that the
Jesuits managed to organize prosperous
economic and cultural life, including printing in the Guarani language.
This was too much for great forces, since this Jesuit-Indian
Republic had shaken the existing "world order." The rebellion was put
down in 1767, which led to the tragedy for Guaranis. The "international
community" managed to achieve interdiction of the Jesuit order in 1773.
But the claim that N.Plantic organized the rebellion is false. Some
sources even claim that the Jesuit Republic was led by Plantic, and
that allegedly a coin was issued with his figure in the Netherlands.
Plantic was never in Paraguay, and never met Guaranis in their
homeland. I owe this info to Mr. Joza Vrljicak, director of Studia
Croatica,
Buenos Aires. The only Croat known to have participated the famous
Paraguay mission was Ivan Krstitelj Marchesetti (or Marqueseti,
1704-1767), born in Rijeka in a noble family having Italian roots,
later croatized. See
- [Zoric, pp. 49-51]
- Mijo Korade and Mirjana Polić Bobić: Paragvajska pisma, Matica hrvatska, Zagreb 2010. (containing a collection of letters by Juan Bautista Marchesetti from Rijeka and Nikola Plantić from Zagreb, published in Croatian and Castillian
- Mijo Korade: Istraživači novih obzorja, Matica hrvatska, Zagreb 2015.
- Mijo Korade, Jerko Matoš and Mira Aleksić: Jesuits and Croatian culture,
Most/The Bridge, Zagreb 1992.
Ivan Pastric (Ioannes Pastritius, Givanni Pastrizio, 1636-1708), Croatian theologist and Hebraist in Rome, redactor of glagolitic books, was born in Poljica near the city of Split. He was cofounder of the Academy of Council in Rome (1671), and among the first members of the famous Accademia dell'Arcadia (since 1691, only six months after its foundation). Giulio Bartolocci, his professor, claimed for Pastric to be the greatest connoisseur of Hebrew language in Rome, and a fine interpreter of Talmud. Congregation de Propaganda Fide entrusted him issuing glagolitic liturgical books (Pastric's Glagolitic breviary was issued in 1688, and Glagolitic missal in 1706). He was very famous for his overall knowledge and humanism. So G.W. Leibniz wrote about him as knowledgeable Pastric, whose humanism I experienced (...doctissimus Pastritius, cuius humanitatem sum expertus). Pastric was a member of the first geographic society in the world: Academia cosmographica degli Argonauti. The last two years of his life he was the president of Croatian Confraternity of St Jerome in Rome.
Benedikt Rogacic (1649-1719), was esteemed Jesuit,
writer and poet from Dubrovnik, who was writing in Latin and Italian.
Among his ethical works we mention his poem Euthymia sive tranquilitate animi (Rome,
1690), in which he celebrates the peace of mind in verse. His most
important prose work is L'Uno
necessario (five folumes, Rome 1697-1708). Both these works had
a great success, especially the first one, which had numerous reprints
and several translations up to these days. See an article by Mijo
Korade: [PDF].
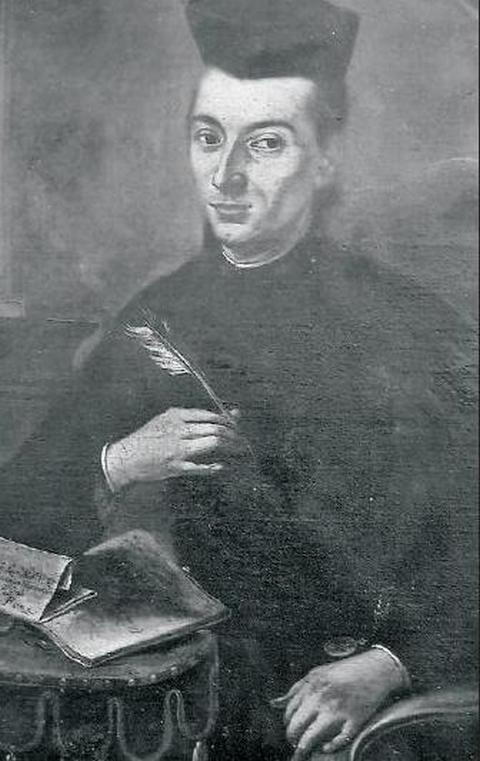

Josip
Marinović (1741-1801). Portrait kept in Gospa od Škrpjela, Boka
kotorska.
Photo by Mijo Korade.
Josip Marinovic (1741 - 1801), was a Jesuit born in Perast - Kotor (in Boka kotorska, annexed to Montenegro in 1945), professor of theology in Venice. His friendship with an Armenian banker Serpos resulted in his interest for the history of Armenians. His assiduous research resulted in the book "Compendio storico...della nazione armena", published in Venice in 1783. The book had a great success. Though it was signed by Serpos, its true author was Marinovic. It represents the first history of Armenians published in Europe. It is interesting that the book had been extended and republished by Ivan Dominik Stratico (1732-1799), bishop on the Croatian island of Hvar. This book incited European interest for Armenian people and their culture. In particular, upon the initiative of the Vatican, supported by Austria and Russia, in 1830 the Turkish sultan admitted very old Armenian Christian Church and allowed Armenian Archdiocese to be founded in Constantinople. See [Gregory Peroche], p. 119.
Vladimir Solovev (or Soloviev, Solovjov, correct reading: Solovyov, 1853-1900), outstanding Russian humanist, religious philosopher and poet, spent a part of his life in Croatia, with Croatian bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer and in Zagreb. In Zagreb Soloviev published his book Istoriya i budushchnost' teokratii (The History and future of Theocracy) in 1886, the first volume of projected (but never completed) three volume work. Let us cite a part of a speech of Pope John Paul II (1 September 1996): For him the very basis of culture was recognition of the unconditional existence of others. Hence his rejection of a monolithic type of cultural universalism, incapable of respecting and accepting civilization's many different expressions. He was consistent with this view even when he became an ardent, impassioned prophet of ecumenism, doing all in his power for reunification between Orthodoxy and Catholicism.

St Leopold Bogdan Mandic (1866-1942, memorial day 30th July)
Ivan Benigar was born in Zagreb in 1883, studied in Graz and Prague, and since 1908 lived Argentina, in Patagonia, among Mapuches or Araucanos Indians. He wrote a dictionary of Mapuche language and several other books. Since 1924 he was a member of the "Council of American history", which is today "National history academy" in Buenos Aires. Married with Eufemia Scheypuquin, grand-daughter of Mapuches chieftain Catriel, he had 11 children. When she died, after 6 years he married again with a Mapuche Indian, and had four children. Due to his intense scientific activity in Latin America, it is not surprising that he earned the title White chieftain of Mapuche Indians. Ivan Benigar and his brother were born in Zagreb, and considered themselves to be Croatians, although their parents were Slovenians, see [Verlichak Vrljicak, Hrvati u Argentini, p. 25].
Aleksa Benigar (Alexius Benigar, 1893-1988), born in Zagreb, was a Croatian missionary in China for 25 years, since 1929 till 1954. He is an author of an extensive monograph about blessed Alojzije Stepinac. His Chinese name was Pen Lin Gan, and he taught theology for three generations of Chinese students in Hankow, several hundred of them. He wrote an extensive two volume work "Liturgia Romana", in Beijing in 1947. He also wrote an extensive work "Theologia spiritualis" in the Latin language, dedicated to blessed Alojzije Stepinac, published in Sapporo in Japan in 1958, reprinted in Rome in 1964). Father Benigar spoke seven languages: Croatian, Polish, Russian, German, Chinese Mandarin, Italian and Latin.
As many as thirty intellectuals from Croatia were members of the famous Accademia dell'Arcadia (Academy of Arcadia) in Rome, founded in 1690 as the literary and scientific circle around the Swedish queen Cristine (in 1925 it assumed the sub-title Accademia Letteraria Italiana). The members obtain the special names inside the Accademia (Inter Arcades). Some of outstanding Croatian members of Arcadia were
- Ivan Pastric (Inter Arcades Ergino Parorio), member of Arcadia only six months after its founding
- Gjuro Baglivi (Inter Arcades Epiduaro Porgense)
- Rugjer Boskovic (Inter Arcades Namenio Anigreo)
- Rajmund Kunic (Inter Arcades Peredao Megaride)
- Adam Aleksandar Patacic (Inter Arcades Sirasio Acrotophorio), member of the Arcadia with only 23 years
- Benedikt Stay-Stojkovic (Inter Arcades Areta Epidaurense)
Important Croatian humanist in France was Mirko Drazen Grmek (1924-2000), historian of biomedical sciences.
Josip Stjepan Poglajen or Tomislav Kolakovic (1906-1992)
 Borislav Arapovic, born in Bosnia
and Hercegovina in 1935, is
honorary director of the Biblical
Institute in Stockholm, Sweden. In 1973 he founded The
Institute
for Translation of The Bible into Languages of (former) Soviet Union.
In 1996 the Russian Academy of Sciences conferred him a doctorate
honoris causa. In 1999 he was elected foreign member of the Russian
Academy of Sciences. For the creation of the Children’s Bible
in
1983, Dr. Arapovic was awarded the Leo Tolstoy medal by the Russian
Children’s Fund. In the period
of 1983-90 ten editions of the Children’s Bible in five
million
copies
were printed for free distribution in Russia.
Borislav Arapovic, born in Bosnia
and Hercegovina in 1935, is
honorary director of the Biblical
Institute in Stockholm, Sweden. In 1973 he founded The
Institute
for Translation of The Bible into Languages of (former) Soviet Union.
In 1996 the Russian Academy of Sciences conferred him a doctorate
honoris causa. In 1999 he was elected foreign member of the Russian
Academy of Sciences. For the creation of the Children’s Bible
in
1983, Dr. Arapovic was awarded the Leo Tolstoy medal by the Russian
Children’s Fund. In the period
of 1983-90 ten editions of the Children’s Bible in five
million
copies
were printed for free distribution in Russia.
He discovered an amazing pacifist sermon given in 1778 by an anonymous Croatian preacher to Croatian soldiers. The sermon was published in German in 1778, in Dutch in 1778 in the Hague, Amsterdam, and Leeuwarden, in Swedish in 1778 in Norrköping, and in 1779 in Stockholm, and in Latvian in Riga - Leipzig in 1804.
Gerardo Zerdin is a Croatian Franciscan born in 1950, and a missionary in Peru since 1975. He is living already for 32 years among Peruvian Indians as a priest, and since 2001 as a bishop appointed by the rescript of Pope John Paul II. Msgr. Zerdin learned several Indian languages, and now basic Christian prayers are available in these languages. Extremely important work is devoted to Indian children, first to teach them to read and write, both in their native languages and in Castellano.
Msgr Zerdin initiated a very complex and notrivial task to start the university for Peruvian Indians, Nopoki - Universidad para indigenas, in cooperation with the Catholic University in Lima. It started to work in 2006/07 with 57 students. The aim is to educate future school teachers for work within their native communities, in order to preserve their roots, language and customs, and ensure material and cultural prosperity.
Croatian Ecumenists
- Ivan Stojkovic de Corvatia (1390/95-1443)
- Andrija Jamometic (~1420-~1486)
- Beniamin (15/16th centuries)
- Marko Antonio de Dominis (1560-1624)
- Juraj Krizanic (1618-1683)
- Ivan Pastric (1636-1708)
- Leopold Bogdan Mandic (1866-1942)
- Vladimir Soloviev (1853-1900)
Croatian Encyclopaedists
Now we have come to a very rich history of the Croatian Encyclopaedia. Its origins go back to the first half of the 15th century.The earliest known lexicographic work is a handwritten book "Liber de simplicibus" (The book about medicinal herbs), prepared in Zadar and Venice between 1415 and 1453. Written by an Italian physician and Zadar protophysicist Nicolo Roccabonelli, it contains very nice drawings of various plants together with their Croatian, Latin, Greek, Arabic and in part German names. It is held in the Venetian national library Marciana.
Ilija Crijevic, poet, orator and lexicographer from Dubrovnik (1463 - 1520), wrote his Lexicon in 1480, a Latin encyclopaedic dictionary. This very nice handwritten book of large format, 33 x 23 cm, has 429 pages.
We know of a small Italian - Croatian dictionary Opera nuova che insegna a parlare la lingua schiavonica alli grandi, alli picoli et alle donne, containing about 300 words, written in 1527 by Pietro Lupis Valentiano in Ancona, Italy.

Pavao
Skalic, photo from Zagreb
Pavao Skalic, a humanist-polyhistorian (Paulus Scalichius, born in Zagreb, 1534-1575), was the first to have used the notion of
in its modern meaning, in his book Encyclopediae seu orbis disciplinarum... (Basel, 1559).

He also wrote a musical tractate "Dialogus en Lyra" (Köln, 1570). He used to write his name as Pavao Skalic de Lika, thus indicating the origin of his family.
 An
extremely interesting biography has Bartol
Gyurgieuits (Bartol Jurjevic or
Gjurgjevic, born in the region of
Turopolje near Zagreb, known for nice wooden churches, 1506 - 1566?), a
participant of the tragic battle on the Mohac field in 1526, where he
was captured by the Turks and lived as a slave in many parts of the
Turkish Empire. As a captive he was a teacher of Greek in Damascus (see
[Marianna
D. Birnbaum, p. 252]). After
13 years of slavery he managed to escape, first finding refuge among Armenians
(see [Marianna
D. Birnbaum, p.
253]). Since
that time he travelled a lot throughout Europe, agitating for the
creation of a strong union against the Ottoman Empire. His numerous
writings in the Latin language were published first in Antwerpen (1544)
and then extensively reprinted in many other languages: Italian,
French, English, German, Spanish, Dutch (Flemish), Hungarian, Polish,
Czech etc. One of his numerous titles is Exhortatio contra Turcas.
These
extremely interesting testimonies about the Ottoman
(Turkish) Empire can be found in the libraries of almost all larger
European cities:
An
extremely interesting biography has Bartol
Gyurgieuits (Bartol Jurjevic or
Gjurgjevic, born in the region of
Turopolje near Zagreb, known for nice wooden churches, 1506 - 1566?), a
participant of the tragic battle on the Mohac field in 1526, where he
was captured by the Turks and lived as a slave in many parts of the
Turkish Empire. As a captive he was a teacher of Greek in Damascus (see
[Marianna
D. Birnbaum, p. 252]). After
13 years of slavery he managed to escape, first finding refuge among Armenians
(see [Marianna
D. Birnbaum, p.
253]). Since
that time he travelled a lot throughout Europe, agitating for the
creation of a strong union against the Ottoman Empire. His numerous
writings in the Latin language were published first in Antwerpen (1544)
and then extensively reprinted in many other languages: Italian,
French, English, German, Spanish, Dutch (Flemish), Hungarian, Polish,
Czech etc. One of his numerous titles is Exhortatio contra Turcas.
These
extremely interesting testimonies about the Ottoman
(Turkish) Empire can be found in the libraries of almost all larger
European cities:
Paris, Rome, Vienna, Basel, Leiden, Wittenberg, Florence, London, Prague, Venice, Antwerpen, Liége, Worms, Nürenberg, Krakow, Lyon, Frankfurt etc. (e.g. in 44 towns of Germany alone) and in some cities of the USA.

Bartol
Gyurgieuvits:
Libellus vere christina lectione dignus diuersas res Turcharum brevi
tradens, Rome, 1552, content:
De Turcarum ritu et caeremoniis, De
afflictionem tam captivorum, Vaticinium infidelium de Christianorum
cladibus et calamitatibus, Deploratio cladis christianorum ad
potentisimos monarchos; the book contains "Our Father" in the Arabic in
written in Latin characters (from the 2006 exhbition
in
NSK, Zagreb)
Most of his writings contain small dictionaries of the Croatian (which he calls Slavonian), Turkish, Persian and Hungarian languages. As a part of his "De afflictione...sub Turcae" (1544) he wrote the first known Croatian - Latin dictionary (with the basic prayers: Our Father, such as Hail Mary, Credo), which is also the first known dictionary among the Croats. He is also the author of the practical Italian - Arabian - Hebrew - Chaldean dictionary, added to the description of his pilgrimage to Yerusalem when escaping from the Turkish slavery. It was written in Italian: "Specchio della peregrinazione delli piu notabili luoghi della Terra Santa", and the author signed it as Georgievicz de Croatia. His name is written in as many as 25 different ways in the literature.
He also mentioned a
Croatian Script, which is "different from
any other script in the world" (Glagolitic).
He
indicates that the Croatian language is spoken among others on the
Constantinople court of Turkish sultans. Gyurgieuivits' works are also
of interest for the study of Islamic music.
He was not only the first Croatian author, but also the first Slav
author whose writings were popular throughout Europe. For more
information see [Zoric].
Branko
Franolic: Georgijevic's Description of Turkish
Ways and Customs:
Unique Work Published in London in 1570,
Croatian Times, London 1977
The Englishman Hugh Goughe wrote "The Ofspringe of the House of Ottomane", published in London in 1570, which is a translation of Gyurgieuits' book "De origine imperii Turcorum". In Goughe's book there is a dialogue in Croatian with a parallel English translation, alongside with two prayers in Croatian (Our father and Hail Mary).

Source
Branko Franolic:
Georgijevic's Description of Turkish Ways and Customs: Unique Work
Published in London in 1570, Croatian Times, London 1977 (many thanks
to Dr. Franolic for sending me this article)
Let us present again Lord's Prayer in Croatian using contemporary orthography.
|
Sveti se
tvoje ime. Kraljevstvo pridi,
tvoja volja budi na zemlji kako na nebu.
Daj nam ga danas našega vsagdanjega
kruha, i odpušćaj nam naše duge, kako mi
odpušćamo našim dužnikom, i ne pelaj
nas v napast, da izbavi nas od
neprijazni, Amen. |
Note that the word order of Croatian follows the word order of English version of Lord's Prayer. The Lord's Prayer in Croatian with the usual word order would be as follows (compare with the Croatian Glagolitic Lord's Prayer, 1375, Bibliotheque nationale in Paris, which is very close):
Otče nas ki jesi na nebesi \\ Sveti se ime tvoje \\ pridi kraljevstvo tvoje \\ budi vlja tvoja \\ kako na zemlji tako i na nebu \\ kruha vsagdanjega daj na ga danas \\ i odpušćaj nam duge naše \\ kako i mi odpušćamo dužnikom našim \\ i ne pelaj nas v napast \\ da izbavi nas od neprijazni, Amen.
There is also a small vocabulary of Croatian language, Vocabula Sclavonica, containing 52 words and phrases. Gyugyieuits himself is called the "first Croatian lexicographer" in this book. The British Library in London holds as many as 44 copies of various Gyurgiveuvits' books.
We should also mention the following book, Georgievits, Bartholomeus: De reitibus et differentiis Graecorum et Armenicorum, Antverpiae?, 1544. (see [Marianna D. Birnbaum, p. 194])
Regarding early dictionaries of the Croatian language, let us mention a German knight Arnold von Harf (1471-1505) who visited the Croatian lands along the coast during his pilgrimage to the Holy Land in 1496-1499. His book "Die Pilgerfahrt des Ritters Arnold von Herff von Cöln", published in Köln in 1860, includes a short conversational dictionary of the Croatian language containing 56 words and basic expressions. He also visited the beautiful, strong and freedom loving city of Dubrovnik (as he says), for which he states to be in the Croatian Kingdom - in den Koenynckrijh van Croatijen.
Another Turkish captive was Juraj Hus (Hosti), contemporary of the above mentioned Bartol Gyurgieuvits. After the defeat of Sultan Suleyman the Magnificent in the battle with the army led by famous Croatian statesman Nikola Jurisic in 1533 (the aim of Suleyman was to occupy Vienna), and after his retreat through Croatian lands, Juraj Hus was taken to slavery from his village (Rasinje) to Constantinople. Since he did not want to renounce his Catholic faith, he managed somehow to be educated as a Turkish military trumpeter. As a musician he visited many lands: India, Egypt, and Holy Land. He described his visit to pyramids near Cairo, where he was playing his trumpet on the top of a pyramid, while soldiers below were measuring the volume of the pharaoh's grave. After many years he managed to escape, and reached Genova, and then Rome, where he was accepted in the Croatian Collegium of St. Jerome. In his village in Croatia he did not find any of his relatives, and died in Pozun (today's Bratislava in Slovakia) around 1566. He left the description of his pilgrims in his manuscript entitled Descriptio peregrinationis Georgii Huszthii. One version of the manuscript is held in the Vatican library, and the other in the National Library in Vienna. For more details see [Zoric].
Faust Vrancic (or Faust Verantius, 1551-1617) from Sibenik was the author of a five language dictionary "Dictionarium quinque nobilissimarum Europeae linguarum: Latinae, Italicae, Germanicae, Dalmaticae et Hungaricae" (Venice, 1595), with more than 5000 words (i.e. altogether 25000 words), where Dalmaticae means Croatian language. Indeed, in his dictionary the words Dalmata, Dalmatia, Dalmaticae are translated as Croat, Croatian land, Croatian respectively. It is known that Vrancic was fluent in at least seven languages. See p. 13 of his Dictionarium:
Faust Vrancic considered that the Dalmatian language was the most beautiful among Slavic languages, and that it was spoken from Adriatic sea to rivers of Drava and Danube. In the second edition to his dictionary, issued in collaboration with a Prague Benedictine Petar Loderecker, the Latin description of Dalmatian language was given as follows: the Croatian language. See [Malic, Na izvorima hrvatskoga jezika, p. 28].

Faust Vrancic (1551-1617), distinguished Croatian inventor and
encyclopaedist, is burried upon his last wish,
on the island of Prvic near the city of Sibenik on Croatian coast.
Vrancic's dictionary is dedicated to Alfonso Carillo, a Spanish Jesuit who supported its publication.
His work was an important source for the creation of several subsequent European dictionaries: Hungarian - Italian dictionary written by Bernardino Bali, "Thesaurus polyglottus" by a German humanist and lexicographer Hieronim Megister (1603, "editio secunda " in 1613), and "Dictionarium septem diversarum linguarum (Videlecit Latine, Italice, Dalmatice, Bohemice, Plonice, Germanice et Ungarice)" written by a Czech Benedictine Peterus Lodereckerus Pragensus in 1605.

Peter
Loderecker: Dictionarium
septem diversarum linguarum, Videlecit Latine, Italice, Dalmatice,
Bohemice, Polonice,
Germanice et Ungarice, Prague 1605
Faust Vrancic was a chancellor on the Court of king Rudolph II in Prague (Hradcany) from 1581 to 1594, where also a famous musician Adrian de Vries, astronomer Tycho Brache, mathematician and astrologer Johannes Kepler were present. He also wrote about logic and ethics. However, his major contributions are related to numerous technical inventions.
Faust Vrancic, scrollable books, National and University Library, Zagreb
Faust Vrancic 1551-1617 Memorial Center on the island of Prvic near the town of Sibenik in Croatia
An interesting and surprising fact about Faust Vrancic's "Dictionarium quinque nobilissimarum Europeae linguarum: Latinae, Italicae, Germanicae, Dalmaticae et Hungaricae", published in Venice in 1595, (i.e., from Dictionary of Five Most Noble European Languages: Latin, Italian, German, Croatian and Hungarian), is that it provides a long list of Croatian (Dalmatian) words which entered into Hungarian vocabulary:

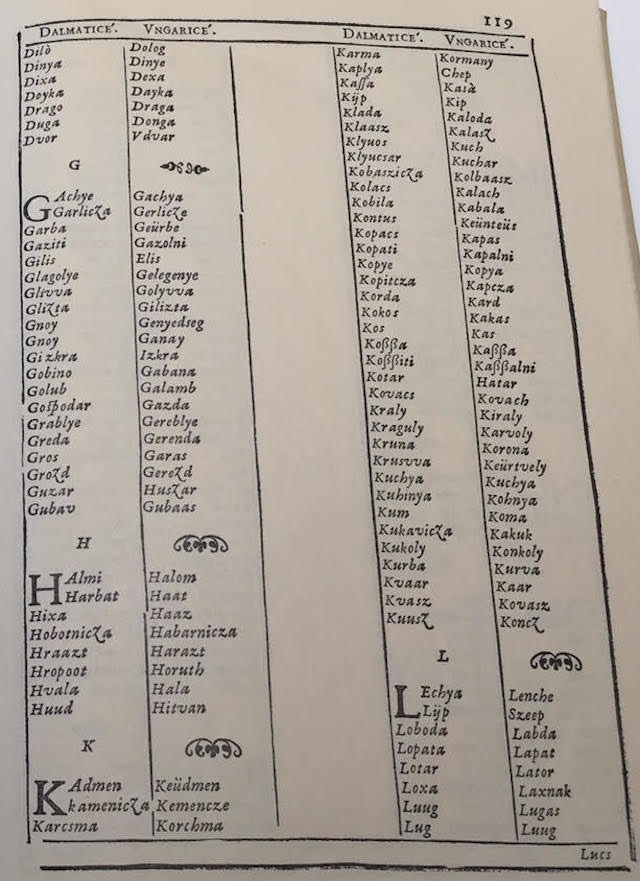
Dictionarium quinque nobilissimarum Europeae linguarum: Latinae, Italicae, Germanicae, Dalmaticae et Hungaricae
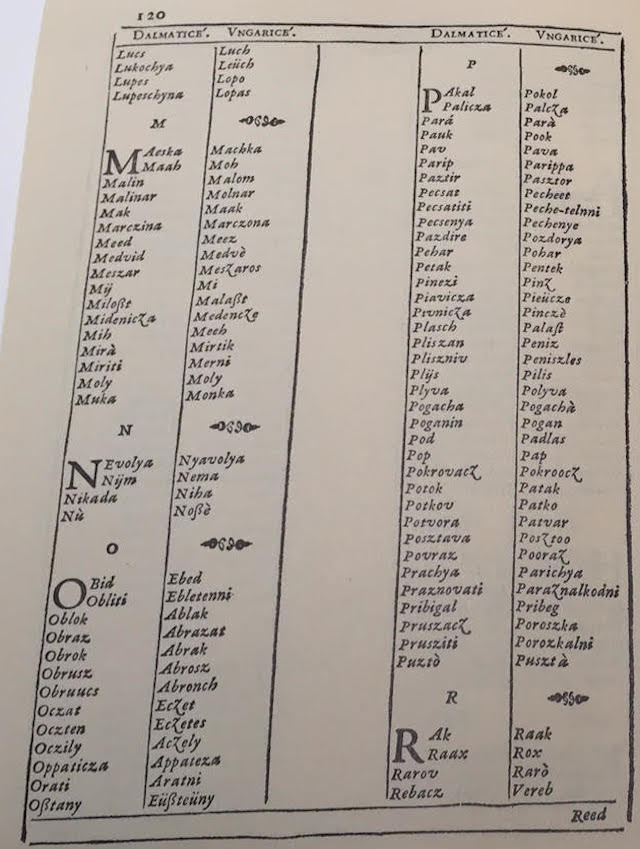

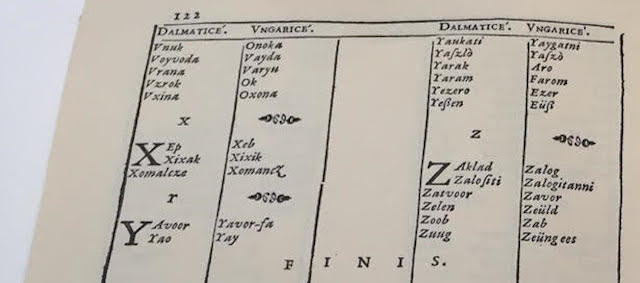
It is surprising that at that time (16-17th centuries), among most noble European languagues in Vrancic's dictionary, there is neither English, nor French, nor Castillian nor Portuguese.

Faust Vrancic also wrote Xivvot nikoliko izabraniih divviicz (The Life of Some Virgins), written in Croatian and published in Rome, AD 1606 (on the above photo, taken in 2017 during the exhibition dedicated to Faust Vrancic, organized by the Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts).
Here, it is worth mentioning that in the beginning of the 17th century (in 1615), a few benedictine nuns in the city of Šibenik appeared as actresses in a local church. They staged the story of Three Magi written in Croatian language by unknown author. This was the first known case in European history of women appearing in a church theatrical play (church displays). Until then, even the roles of women had been played by male actors. Information by Mrs. Zlatka Rodin during her lecture about Faust Vrančić, delivered in the Memorial Centre Faust Vrančić on the island of Prvić near Šibenik in August 2024. This is described in more detail in the following references:
- Krsto Stošić: Benediktinke u Šibeniku, Šibenik 1994.
- Petar Kolendić: Građa za povijest književnosti Hrvatske, knjiga 7., JAZU, Zagreb 1912. u tekstu naslova Predstava "Triju kralja" u Šibeniku g. 1615. (tu se nalaze najpotpuniji podatci)
- Ivo Livaković: Kazališni život Šibenika, Šibenik 1984.
In 1605 a Czech Benedictine Petr Loderecker published the book Dictionarium septem diversarum linguarum: videlicet Latine, Italice, Dalmatice (Croatian), Bohemice, Polonice, Germanice & Ungarice... in Prague (around 5000 words for each language). This dictionary represents an extension of Vrancic's 1595 Dictionary of the five most noble European languages: Latin, German, Italian, Croatian and Hungarian, in which Czech and Polish languages have been added. In Loderecker's book we can find the following descriptions: Dalmatian = Croat, Dalmatia = Croatia, Dalmatian = Croatian.
The book is a result of collaboration between Faust Vrancic and Loderecker, which represents the earliest known lexicographic collaboration in Central Europe. Loderecker's dictionary has 578 pages: the first 200 pages consits of Latin vocabulary translated into Italian, Croatian, Czech, Polish, German and Hungarian (in this order), while the remaining 378 pages consist of vocabularies of Italian, Croatian, Czech, Polish, German and Hungarian translated (in this order) into Latin.
Faust Vrančić was at the
court of the Roman-German Emperor
and Croatian-Hungarian King Rudolph II, who was crowned by Antun
Vrančić, Faust's uncle. Now doubt, these are some of the reasons why in
the chruch of st. Vitus in Hradčani Cathedral in the Prague, we can see
fantastic Croatian Coats of Arms. Karl of the Stier (Karlo
Štajerski), brother-in-law of King Rudolph II, was in charge
of
the Croatian Military Frontier, where in 1578 he made the foundations
of the new very strong fortress of Karlovac, which was important in the
struggle of Croatia against the Turkish Ottoman Empire onslaughts.
Among numerous great artists and scientists at the Royal Court in
Hradčani, Faust Vrančić, the Royal Secretary, was in close contact with
Tyho de Brahe and Johannes Kepler.
Lit.: Vladimir Muljević: Hrvatski znanstvenici Faust i Antun Vrančić, Encyclopaedia Moderna, 2(42) (1993), pp.122-136.
A significant Croat, born on the island of Hvar, very little known even among the Croats, was Ivan Franje Bjundovic (Giovanni Francesco Biondi, 1573-1645). After having met Sir Henry Watton, English ambassador in Venice, with whom he shared the same interests as a lawyer and literature fan, he journeyed to England and carried confidential messages to King James I. Obviously, he was considered a competent scholar and diplomat, since James himself entrusted him with important diplomatic missions.
Bjundovic wrote a trilogy in Italian: "Eromena", "La danzella desterrada" and "Il Corlabo", which had several editions. Their English translations enjoyed exceptional popularity, as well as German and French. His most important work is "History of the English Civil Wars", with his name appearing as Sir Francis Byondy. It was published in three volumes, where he described the Wars of the Roses. It was first published in Italian (L'istoria della Guerre civili d'Inghilterra) and printed in Venice in 1637-1644. Its English translation started to appear in 1641.
Bartol Kasic (1575-1650), a Croatian Jesuit, was the author of the first Croatian Grammar "Institutiones lingue illyricae", printed in Rome 1604. About the same time he prepared the Croatian - Italian dictionary, which remained unpublished until 1990. In the period of 1631-1636 he translated the whole Bible into spoken Croatian, but unfortunately the book remained only in handwriting. In his "Ritual Rimski" ("Rituale Romanum", Rome, 1640) he cites very old Croatian names for months that are in use even today (more about this):
|
- In 1999 we celebrated four centuries of Croatian philology, which has started with Bartol Kasic. His work was very important in standardization of the Croatian language, using the principle "write as you speak".
- He also wrote one of the earliest autobiographic books in Croatia describing the consequences of the Turkish Ottoman occupation. In one of his writings he concludes: I stop here, crying and sighing when I remember all that I saw with my own eyes: profaned churches, settlements completely destroyed, so that nothing was left except tents, hovels, huts. Let God have mercy on us and let him bless us... Let him illuminate us with his Face and Word, and let him have mercy on Croatian people, which is crushed and almost heart-broken.
- In 1612 he opened the gymnasium for the Catholic youth in Belgrade (mostly for children of native Catholics and the Dubrovnik merchants). At that time Belgrade was under the Turks. This was the first gymnasium in Serbia.
- Two samples of Kasic's Cathecism are held in Bibliothéque Nationale (former Bibliothéque Royale) in Paris, France.
- For more information see Vladimir Horvat: Bartol Kasic; cetiri stoljeca hrvatskog jezikoslovlja, Zagreb, 1989. In this book you can also find important information about Dominican Glagolitic priest Beniamin de Croatia.
- It is interesting that in Kasic's dictionary one can find the name of "tesla", meaning adze. One of grand-grandfathers of the famous inventor Nikola Tesla was Draganic, nicknamed Tesla. I owe this information to dr. Vladimir Muljevic, professor emeritus of the University of Zagreb.
Jakov Mikalja (Giacomo Micaglia, ~1600 - 1654) was lexicographer and theological writer born in Peschici in Italy in Molise (the name of Peschici is obviously of Croatian origin), collaborator of Bartol Kasic. He was descendant of Croatian exiles that had to escape before the Turks from Dalmatia. After his studies he lectured at the Jesuit collegium in Dubrovnik. His most important work is a dictionary Blago jezika slovinskoga containing 25,000 words (Thesaurus linguae Illyricae sive Dictionarium Illyricum, 1649, printed in Loreto and finished in Ancona in 1651), and also Croatian-Italian-Latin dictionary with grammar, containing rich vocabulary of Croatian ikavian - chakavian and stokavian words. In this huge book having 926 pages, which starts with Croatian column, he clearly stated to be Croat. His surname is derived from his father's name (son of Mikalj), so that Mikalja is genitive case of Mikalj. His book Ortografija jezika slovinskog represents the first printed orthography of Croatian language. He also published Bogoljubno razmisljanje od Ocenasa in Pozun (= Bratislava) in 1642. The only known copy of this book, printed in Croatian language, is held Bibliothéque Nationale in Paris (within section of Slovak literature!). It is interesting that Mikalja founded the first school for Croatian children in Temisoara in Romania.
Vladimir Horvat: Jubileji leksikografa Mikalje
In Loreto there is a Croatian collegium
founded in 1580.
Ivan Lucic, or Lucius (born in Trogir, 1604 - Rome, 1679) was the founder of modern Croatian historiography, with his major work "De Regno Dalmatiae et Croatiae libri sex" (Amsterdam, 1666). However, the oldest Croatian historigraphic work is Croatian Chronicle, written by Grgur of Bar in the 12th century.
photo
from Croatian
Historical Musem
Map dedicated to Petar Zrinski, ban of Croatia. The map was created at the workshop of Joannes Blaeu in Amsterdam as an addition to the work by Ivan Lucic, "De Regno Dalmatiae et Croatiae libri sex", Amsterdam, 1666. Blaeu had inserted the map in Atlas Maior in 1667, and dedicated it to the Croatian ban Petar Zrinski (bottom of the map, in the middle):
To the most illustrious and noble lord, Prince Peter of Zrin, the ban of the Kingdom of Dalmatia, Croatia and Slavonia, hereditary ban of the Littoral, hereditary captain of the Legrad fortress and Medimurje peninsula, master and hereditary prince of Lika, Odorje, Krbava, Omis, Klis, Skradin, Ostrovica, Bribir etc.., Master of Kostajnica and the sliver mine at Gvozdansko, councillor and chamberlain to his anointed imperial majesty, master Ioannes Blaeu dedicates this map.
Text from Croatian Historical Musem. Note Croatian coat of arms on the map.

"De
Regno Dalmatiae et Croatiae libri sex"
(Amstelaedami, 1666),
by Ioannes Lucius
Ardelio Della Bella published his Italian-Latin-Croatian dictionary (Dizionario italiano, latino, illyrico) in 1728, with the grammar of the Croatian language.
Also very important are the following two Croatian lexicographers:
- Ivan Belostenec (born in Varazdin, 1594-1675), who wrote "Gazophylacium seu Latino-Illyricorum onomatum aerarium" published in Zagreb in 1740. It provides a lexical wealth of three Croatian dialects: kajkavian, stokavian and chakavian. This monumental book which has 2000 pages and more than 40,000 words is important not only for Croatian but also for European cultural history: at that time a similar dictionary existed only in Florence, prepared under uncomparably better conditions. Belostenec was a Paulist monk in Lepoglava, who spent part of his life in Croatian south, including Istria. This is also reflected in his dictionary. An incomplete copy of his book Deset propovjedi o Euharistiji (published in Graz in 1672) is held in the University Library of Budapest. Although Belostenec originally used the name of "Croatian language" everywhere in his book, its every occurence was changed due to political reasons to "Illyric language". The book was issued 65 years after his death. According to dr. Olga Sojat the original title of his book was Dictionarium Latino-Croaticum, see [Sekulic, p. 350]
- Andrija Jambresic (1706-1758), who wrote an important lexicographic work Lexicon latinum interpretatione illyrica, germanica et hungarica (illyric = Croatian), published in Zagreb (1742). Jambresic called himself Croata Zagoriensi, as can be seen on the front page of the book. The book contains many valuable historical comments and is imbued with a deep patriotic feeling.
Related to the famous Paulist convent in Lepoglava is Hilarion Gasparotti (1714-1762), born in the lovely town of Samobor near Zagreb. As a Lepoglava Paulist he wrote an encyclopaedic masterpiece Czvet Szveteh (The Flower of Saints) in 4 books on as many as 3,800 pages (982+923+987+896), published in Graz (written as Gradecz there, which reveals the Croatian origin of the name of Graz: grad - town) in 1752, and in Vienna in 1756, 1760 and 1761. In these books he wrote biographies of numerous saints in the beautiful kajkavian Croatian language, which he calls simultaneously slovenski jezik and horvatcki jezik. As we see, at that time Slovenian and Croatian languages were identified. On the front page Gasparotti stated that he consulted sources written in Spanish, Latin, French and German (see [Sekulic, pp 412-415]). Of course, he had at his disposal a magnificent library of the Lepoglava convent. The library and the valuables of the convent have been robbed by Austrian officials after cancelling the Paulist order in Croatia in 1786. This top monument of Croatian culture served as prison during the Yugoslav communist period.
In 1999 a new jewel of Croatian lexicography was discovered: Ljudevit Lalic (17th century) and his handwritten Latin-Italian-Croatian dictionary, Blago jezika slovinskog...Thesaurus linguae illyricae sive Dictionarium Illyricum..., prepared in the period between 1680 and 1696. The book has about 1900 pages, and Croatian words are written in two old scripts: Croatian Cyrillic and Croatian Glagolitic. Ljudevit Lalic was a Franciscan, and the oldest known Herzegovinian lexicographer. For more details see an article by Andrija Nikic in Hrvatsko Slovo.
Ivan Krstitelj Lalangue (= John the Baptist Lalangue), a native of Luxembrug born in 1743, found his new homeland in Croatia in the lovely city of Varazdin, where he was working as a physician until his death in 1799. He wrote an interesting book "Medicina ruralis iliti Vrachtva ladanyszka", 374 p., a medicinal manual which represents an important monument of the Croatian (kajkavian) literature. It contains a botanical dictionary with a description of 160 medicinal herbs in Croatian, including their Latin and German names. It was printed in Varazdin in 1776. Lalangue is also the author of two other books printed in Varazdin.
Julije Bajamonti (1744-1800) was medical historian, writer, translator, encyclopaedist, historian, philosopher, and musician. He composed the first opera in Croatia (performed only once), wrote the History of Split (unfinished and unpublished). Bajamonti helped Alberto Fortis with his journey round Dalmatia, and with his discovery of Hasanaginica. His wife was a Split commoner Ljuba. After the fall of Venice in 1797 he urged that Dalmatia should be annexed to Croatia (and Austro-Hungary). In his speech in 1797 he said that Austria was the successor of the old Croatian state. Like many other Croatian intellectuals along the Croatian coast, Bajamonti wrote most of his works in Italian. Despite this, he certainly felt himself a Croat (or Illyiran, as they said at the time). He was very interested in the Croatian language, national costumes and tradition, economic and cultural progress. See D.Keckemet, E. Stipcevic: Julije Bajamonti, Croatian P.E.N Centre, Zagreb - Split, 1997, p 16. Nicolo Tommaseo claims that there was no one in Italy writing better than Bajamonti in his time.
He performed his medical work in Split, Kotor (in Boka kotorska in today's Montenegro), and Hvar.
The beginning of the Bosnian historiography is represented by a work of rev Filip Lastric (1700-1783), Bosnian Franciscan and Latinist, "Epitome vetustatum provinciae bosniensis", published in Venice in 1765. His "Testimonium Bilabium", published also in Venice in 1755, has been studied in detail by a young Italian scholar Ruggero Cattŕneo, see the summary of his extensive work

Adam Patacic, bishop of Petrovaradin and Calocz archbishop (in Hungary) wrote Latin-Croatian and German dictionary in 1772-1779: "Dictionarium latino-illyricum et germanicum" (illyricum=Croatian, in the kajkavian dialect).
Rev. Marijan Lanosovic published his "Neue Einleitung zur slavonischen Sprache", with the German-Croatian dictionary. The first two editions appeared in Osijek in 1778 and 1789, and the third in Budim (today's Budapest) in 1795.
Josip Voltic (Voltiggi, 1750-1825), an Istrian writer and lexicographer, published the Illyrian (Croatian)-Italian-German dictionary in Vienna in 1803.
A three language encyclopaedic lexicon (Latin, Croatian, Italian) of Joakim Stulli (1730-1817), Franciscan from Dubrovnik, written in three parts on 4721 pages, was an important source of traditional Croatian words, especially in medicine. It was finished in 1810, after more than a half of century of systematic work. Its second, Croatian part, contains about 80,000 lexical units. The dictionary describes among others the meaning of Illiric: Illiric = Croatian.
The Illyrian (Croatian)-French dictionary, prepared by Sime Starcevic (from Udbina in Lika), has been published by the French rulers in Trieste in 1812.
Nicolo Tommaseo was an important writer, lexicographer and politician, born in Sibenik, of Italian nationality (1801-1874). In 1830 he published "Nuova dizionario di sinonimi della lingua italiana", and his voluminous "Dizionario della lingua italiana" in 1865-1879. He was also translating from Latin and Greek into Italian. In 1841-42 he published his "Canti popolari toscani, corsi, illirici, greci". In accordance with his Dalmatian autonomistic views, he believed in the separate "Dalmatian nationality", and was against the unification of Italy, and against unification of Dalmatia with banska Croatia (1861). He also violently criticized the French centralism. It is worth mentioning his close ties with many Croatian intellectuals, especially with Ljudevit Gaj and Ivan Kukuljevic-Sakcinski. With his beautiful elegiac and poetic work written in the Croatian language - "Iskrice" (Sparklets), and published in Zagreb in 1884, he entered the history of Croatian literature. Another important work is his elegy written in the Croatian ikavian language: "Suze sina zahvalnoga." He also wrote pedagogic and philosophic treatises.
Bishop Angelik Juraj Bedenik (1818-1866), Croatian missionary in India. Born in Koprivnica, died in Agra.
Bohoslav Sulek (1816-1895), Slovak by birth, one of the most important Croatian linguists and lexicographers, made an enormous contribution to the enrichment of the Croatian literary language. He invented several hundred new terms that can be seen in his extensive dictionaries: German - Croatian (1860), Croatian - German - Italian Dictionary of Scientific Terminology (1874/75) and other. Many of them are now everyday Croatian words. Some of them also entered other South Slavic languages, including Serbian.
Dragutin Antun Parcic (1832-1902) was a Glagolitic priest, linguist, philologist, and lexicographer born in the lovely town of Vrbnik on the island of Krk, important site of Croatian Glagolism. He wrote extensive Croatian - Italian and Italian - Croatian dictionaries ("Rjecnik ilirsko - talijanski," Zadar, 1858, its last edition was printed under the title "Rjecnik hrvatsko - talijanski," 1901; "Vocabolario Italiano - Slavo," Zadar 1858-68). His 1901 dictionary contains 90,000 words on 1200 pages. He also published a grammar of the Croatian language in Italian: "Grammatica della lingua slava (illirica)", Zadar 1873. Only four years later it was translated into French, but under the title "Grammaire de la langue Serbo-Croate" (sic!) (Paris 1877, Paris 1904). It is little known that he introduced the name of BRZOGLAS for telephone in his dictionaries (Anic's contemporary dictionary claims in all its four editions that "brzoglas" is an NDH neologism, which is not true).

Rimski
Misal - Missale Romanum,
Rome 1893, prepared by Dragutin Parcic, printed in Croatian Glagolitic
Script
His probably most
interesting work is the Glagolitic Missal
that he prepared for the needs of the Croatian
Glagolitic Liturgy, published in
Rome in 1893. See an article
by Igor
Gostl for more details (in
Croatian), or his
book.
Parcic was also one of the first Croatian photographers. Here is his
seal from his photo, written in part in Croatian Glagolitic Script:

Dragutin Parčić
svjetloslikar
na
Galevcu
1863.
(many thanks to Mirna
Lipovac for the photo)
Ivan Dezman (1841-1873) physician, a medical writer and lexicographer, published the first Croatian medicinal dictionary (Rjecnik lijecnickog nazivlja; Croatian - German, German - Croatian) in 1868 in Zagreb.
The reader may be surprised to see such a quantity of old dictionaries of the Croatian language (various grammars are even more numerous). See a remark on the "Declaration about the Name and Position of the Croatian Literary Language", written by outstanding intellectuals and most important cultural institutions in Zagreb in 1967.
According to Edward Stankiewicz (ed): Grammars and Dictionaries of the Slavic languages from the Middle Ages up to 1850: an annotated bibliography, Berlin, Mouton 1984, pp 77-93, Croatians have
- 43 grammars
- 45 dictionaries
The first etimological dictionary among the Slavs is Pravoslovnik by Petar Katancic (1750-1825), which has 1,473 pp (later renamed Etymologicon illyricum by Grgur Cevapovic). The manuscript contains 53,000 entries from A to Svemoguc. See [Franolic, p. 30].
The Croatian language was often designated under the name of Illyrian, Slavonian, Sclavonian, Dalmatian language. For example, rev Emerik Pavic in his 1778 translation of "Flos Medicinae" from Italian (it was the book about health care) wrote to be versified in "Croatian or Dalmatian language". Croatian Franciscan Filip Grabovac (1699 - 1749) wrote a book Cvit razgovora naroda, i jezika ilirickoga, aliti arvackoga, published in Venice in 1747, that is, Flower of people's speech, and of Illyric language, or Crotian.
The voluminous Wurzback's Biographic Lexicon of Austrian Kingdom, prepared in 60 volumes between 1856 and 1891, comprises 24,200 biographies. According to investigations of dr. Igor Gostl as many as 1050 of them refer to the Croats.
Safvet-beg Basagic (1870-1934) was outstanding Muslim-Croatian poet, orientalist, historian and lexicographer. He studied oriental languages and history in Vienna, where he defended his thesis in 1910. His most important work is "Znameniti Hrvati Bosnjaci i Hercegovci (The famous Croatian Bosniaks and Herzegovinians), published by Matica hrvatska (Matrix Croatica) in Zagreb in 1931. In this lexicon he presented nearly 700 biographies. He occupied the position of curator of the Zemaljski muzej in Sarajevo (1919-1927), and was also vice-president of the Sabor (Parliament) of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The first Croatian general Encyclopaedia was prepared in Osijek in 1887-1890 (in two volumes, 600 pages each, from A to G). The project was initiated by Ivan Zoch (1843-1921) and Josip Mencin (1856-1900). Ivan Zoch was the Slovak by birth, who devoted most of his life to his second homeland - Croatia.
One of the greatest projects in this field was the creation of the Croatian Encyclopaedia, initiated in 1938 in Zagreb by Mate Ujevic (1901-1967), but unfortunately the war did not permit our scientists to complete this enormous job. Only five volumes of the highest typographical quality were issued (1941-1945), from A to Elektrika, out of 12 planned volumes. The Encyclopaedia was written according to highest scientific standards, and contains no traces of anti-Semitism, though the ustasha regime in Croatia, being subdued to fascist Italy and Germany, was anti-Semitic. Mate Ujevic was the greatest Croatian lexicographer of the 20th century.

Furthermore, it is known that even some outstanding Serbian scientists wrote their contributions for the Croatian Encyclopaedia from Belgrade during the WW2! The scientific committee was divided into 52 sections, covering among others themes like Judaica (dr. Lavoslav Sik), Serbian life, culture, history and art (dr. Milan Budimir from the University of Belgrade).

Artistic advisor of Croatian Encyclopaedia was distingusihed Croatian sculptor Ivan Mestrovic, while artistic editor was Joza Kljakovic. Outer design had been entrusted to Vladimir Kirin, and magnificantly realized. Volume 1 of this monumental encyclopaedia had 808 pp., 22 x 29 cm. See the list of editors of the main areas, [JPG].

Volume 1 was published by the Konzorcij hrvatske enciklpedije (Consortium of Croatian Encyclopaedia), while subsequent four volumes were published by the HIBZ (Hrvatski izdavalački bibliografski zavod - Croatian Publishing Bibliographic Institute), directed by Mate Ujevic.

Photo
from Wikipedia
It is also interesting that the whole Encyclopaedia (with exception of the last, fifth volume, issued in 1945) was written in phonetical orthography, contrary of the official etymological orthography adopted in 1941, which was regulated by a special law under insistance of Mate Ujevic at president Ante Pavelic. The whole edition has been systematically destroyed by the Yugoslav communist regime, when the Second World War finished. At the same time, Mate Ujevic left without job for almost a year.

Mate Ujevic, posrednik izmedju stare i nove domovine

Mate Ujevic is one of Croatian Righteous. Namely, risking his own life and the lives of his large family, he saved Manko Berman, outstanding architect and member of the Jewish community in Zagreb, from the infamous Jasenovac concentration camp. He intervened also at Archbishop dr Alojzije Stepinac (who openly declared for Jasenovac to be the greatest shame of the Croatian state), and then authoritatively asked at president Pavelic for his release, since he considered him as one of key collaborators for realization of the Croatian Encyclopaedia. Additional information about Ujevic is here (in Burgenland Croatian).
Some of the collaborators of Croatian Encyclopaedia (1938-1945) were: Josip Andreis, Josip Andric, Stjepan Antoljak, Ljubo Babic, Josip Badalic, Antun Barac, Miho Barada, Slavko Batusic, Albert Bazala, Julije Benesic, Franjo Bosnjakovic, Antun Bonifacic, Danica Bresler, Franjo Bucar, Ramiro Bujas, Rudolf Cesarec, Antun Dabinovic, Jean Dayre, Olinko Delorko, Milislav Demerec, Mladen Dezelic, Franjo Dugan, Matija Evetovic, Franjo Fancev, Vladimir Filipovic, Stanko Flögl, Vinko Foretic, Miroslav Freiberger, Milovan Gavazzi, Petar Grgec, Stjepan Gunjaca, Josip Hamm, Ljudmil Hauptmann, Stanko Hondl, Stjepan Ivsic, Ljudevit Jonke, Ljudevit Jurak, Dragutin Kniwald, Franjo Kogoj, Mihovil Kombol, Dervis Korkut, Hamdija Kresevljakovic, Gjuro Kurepa, Emilije Laszowski, Josip Loncar, Radoslav Lopasic, Vatroslav Lopasic, Dominik Mandic, Petar Mardesic, Zeljko Markovic, Alija Nametak, Vilim Nice, Grga Novak, Marko Oreskovic, Stjepan Pavicic, Dusan Pejnovic, Drago Perovic, Mihailo Petrovic, Josip Poljak, Bare Poparic, Vladimir Rozov, Janko Simrak, Bozidar Sirola, Petar Skok, Stjepan Skreblin, Andrija Stampar, Vjekoslav Stefanic, Gjuro Szabo, Mate Tentor, Pavao Tijan, Ciro Truhelka, Fran Tucan, Mate Ujevic, Vladimir Varicak, Dusan Zanko, Vinko Zganec, Nikola Zic, Stjepan Zimmermann, and many other. More than 360 names in Volume I only.

After 1945 Zagreb was again the center of encyclopaedic activity, as a continuation of a very long tradition, with many publications and books being issued during the past 40 years. Here we should mention Miroslav Krleza (1893-1981), one of the most outstanding Croatian writers of the 20th century. The famous French writer Jean Paul Sartre admitted that Krleza has anticipated his idea of the "nausée". During many years Krleza was the president of the Yugoslav Lexicographical Institute in Zagreb (today Lexicographical Institute Miroslav Krleza) and editor in chief of the Encyclopaedia of Yugoslavia. He also signed the important Declaration about the Name and Position of the Croatian language in 1967. Contemporary Croatian Encyclopaedia is available online.

Foreign translations of books written by
Miroslav Krleža: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
The following
book has been donated to the British Queen Elisabeth II.
Five centuries of the Croatian lexicographic work can endure any serious critical judgement, which ranks it to the highest achievements of European lexicography (Igor Gostl). This unusual situation is especially striking in view of the fact that the Croats represent a small European nation.
The Croats organized all the expositions of the (ex)Yugoslav art in Paris:
- in Petit Palais (1919) by Ivan Mestrovic,
- in Palais de Chaillot (1950, L'art médiéval yougoslave) by Miroslav Krleza,
- in Grand Palais (1971, Huit millénaire d'art en Yougoslavie) by Miroslav Krleza, which received 150,000 visitors; it has been considered as "l'événement de la saison" in Paris.
An exposition of the French art has been organized in Zagreb in 1940.
The most exhaustive monographs dealing with the history of Croats in Bosnia - Herzegovina are those prepared by the cultural society Napredak, Sarajevo, and three monographs written by Dominik Mandic, see here.
Pavao Tijan (1908-1997) was a Croatian encyclopaedist born in the city of Senj, close collaborator of Mate Ujevic on the project of Croatian Encyclopaedia (1938-1945). In 1945 he emigrated to Italy, where he published his book Martyrium Croatiae, Rome, 1946. In Spain he was a university professor in Madrid, and known as don Pablo Tijan Roncevic.

He is a holder of the prestigious medal of the Spanish King - Cruz de Alfonso X el Sabio (Encomienda con Place de Alfonso X El Sabio del Estado espanol por sus meritos en el campo de la cultura). Although being a foreigner, he was
- technical redactor of Encyclopedia de la Cultura Espanola, 1-5, Madrid, 1963-1968,
- close collaborator of editor in chief of the biographic encyclopaedia "Forjadores del Mundo Contemporaneo" (Forgers of the Contemporary World), 1-4, Madrid, 1959-1961,
- collaborator in Las grandes corrientes del pensamiento contemporaneo, Madrid, 1959, I, II,
- collaborator of Geografia Universal, Barcelona 1952.
- Proceso de formación de las naciones eslavas, Madrid, 1952
- Crisis del liberalismo en al Europa Central, el mito Masaryk, Madrid, 1958 (429 pp)
- La formación de las naciones balcanicas de hoy, Madrid, 1947
- La historiografia rusa dirigada por los Soviets, Madrid, 1949
- Evolucion del ideal eslavo en los ultimos cien anos, 1949
- El mito Masaryk, 1951
- Salamanca en la tradicion cultural croata, 1953
- Constantinopla y su imperio, 1954
- Ivo Andric, premio Nobel de Literatura 1961, 1962
Nedjeljka Luetić Tijan: Život Pavla Tijana, Matica hrvatska, Zagreb 2014. ISBN 978-953-150-935-0

The town of Senj, Pjevačko tamburaško društvo Orlovo gnijezdo (Singing Tamburatza Society Eagle's Nest),
Ožegovićianum School in Senj, 1919/1920. In the second row, 2nd from the left, is Pavao Tijan
(distinguished Croatian lexicographer) playing bisernica. Source of the photo [Tijan].
Premio Brajnovic a la communication is a prestigious Spanish award (500,000 pesets) established in 1997 upon the initiative of newspapermen and lecturers from the University of Pamplona as a recognition to Luka Brajnovic (born in 1919 in Kotor, in Boka kotorska in today's Montenegro, died in 2001). He was a professor of Ethics at the University of Navarra, a former director of the Institute of Artes Liberales, a well known Spanish intellectual. It is interesting that the award was established during his lifetime.

Professor
Brajnovic on the
right, Prof. Radovan Grgec, Mrs Brajnovic,
and the King
of Dolls on the left, in
Pamplona (many thanks to Prof. Grgec)
He was the founder and the dean of the prestigious School of Communication at the Universtiy of Pamplona (Facultad de Comunicación de la Universidad de Navarra) until his retirement, and he educated hundreds of top newspapermen working in Spain and in Latin America. Luka Brajnovic is the author of important monographs, like
- Tecnologia de la informacion, 1968
- Deontologia periodista, 1969
- Literatura de la revolucion bolschevique, 1975
- Despedidos y encuentras.

![]()

- One of his brothers was killed by Yugoslav partisans on the islet of Daksa near Dubrovnik in 1944, sharing the same destiny as the whole group of forty four leading Dubrovnik intellectuals.
- Premio Brajnovic for 2001 was conferred posthumously to Sinisa Glavasevic, Croatian newspaperman killed in Vukovar in 1991 during the Greater-Serbian aggression on Croatia. Exhumed from the mass grave Ovcara near Vukovar together with several hundred detainees from the city hospital.
- Premio Brajnovic for 2005 was conferred to Dr. Joaquin Navarro-Valls, director of The Holly See Press Office, The Vatican. It is interesting that he studied among others at the Faculty of Sciences and Communication in Pamplona where Luka Brainovic was teaching.

Photo
from Faculdad de Comunicacion
(School for
Communication)
Universidad de Navarra
|
The Luka Brajnovic Award for Communication was inaugurated by the School of Communication at the University of Navarra in 1997. The award was established in memory of Luka Brajnovic –who died on the 8th February 2001– as a mark of respect to his career, his professional standing and reputation. Journalist, writer and Croatian poet resident in Spain after World War II, Luka Brajnovic was professor of more than thirty generations of journalists in the University of Navarra and first author of an Information Deontology manual written in Spanish. The Award is bestowed on those who have defended human dignity and the fundamental values of freedom, tolerance and solidarity in their work in the field of communication. Thus far, the award has been granted to the following people:
Don Luka, my professor, by Carmen Ripa |

Luka
Brajnovic among his students in Pamplona,
Spain (source)
|
Luka Brajnovic Davinovic was born in Kotor, Croatia, in 1919. He studied law in Zagreb, and was president of the League of Croatian Students. When Communism took over his country, he was persecuted for the faith and risked his life with Christian heroism on various occasions. He was forced to leave his country and spent twelve years without being able to see his wife and daughter. He managed to reach Italy, where he met Blessed Josemaria. He later moved to Spain, and resided there until the end of his life. He joined Opus Dei in 1952. In 1960 he became a professor in the School of Journalism at the University of Navarre. He was noted for his simplicity, good humor and spirit of service. He died in Pamplona on February 8, 2001. |
Luka Brajnovic: Despedidas y encuentros / Memorias de la guerra y el exillio, EUNSA - Ediciones Universidad de Navarra, 2001, 2nd edition also exists (Croatian translation published in 2019: Oproštaji i susreti / Sjećanja iz rata i izgnanstva)
Josip Bratulic: Luka Brajnovic - krizni put hrvatskog intelektualca, in [Boka kotorska - jedno od izvorista hrvatske pasionske bastine, pp 199-210]
Ivan Illich (1926-2002) was Croatian-Jewish philosopher and social critic, born in Vienna, baptized in Croatia in the city of Split (in the Cathedral of St. Dujam - Domnius). His mother was Jewish (Ellen b. Regenstreif-Ortlieb) and his father Croatian (Petar Ilić). With his grandfather, he spent his youth (since the age of three months) on the island of Brač near the city of Split until 1936, learning Italian, French and German, as well as Croatian. Later, he has learned Ancient Greek and Latin, Spanish, Portuguese, English, Hindi, and some other languages. Some of his most importan books are
- Deschooling Society, 1971
- Tools of Conviviality, 1973
- Energy and Equity, 1974
- Medical Nemesis, 1975
His books were translated into at least 25 languages.
- IVAN ILLICH – (English Subtitles) Un Certain Regard – A 1972 Interview
- Ivan Illich | Part Moon, Part Travelling Salesman: Conversations with David Cayley (1989), duration 4.5 hours
- Ivan Illich sur l'école
- Shalini Suryanarayan (India): Education and society - Ivan Illich; the corresponding video for students
- Colin McDonald: Illich in the valley : applying conviviality as a lens for development in tribal India
- JEDAN OD NAJPOZNATIJIH I NAJUMNIJIH HRVATA U SVIJETU Kršćanska »konvivijalnost« Ivana Illicha (Glas koncila)
- Ivan Illich (Wikipedia)
For additional information see
- A short survey of encyclopaedia making in Croatia, by Lexicographic Institute, Zagreb.
- A compendium of Croatian literary resources on the web from Renaissance to the end of 19th century (provided by AATSEEL)
- Circulus Latinus Zagrabiensis
- Mirko Tomasović: Nove
slike iz povijesti hrvatske književnosti, Matica hrvatska,
Zagreb 2008.
- Mirko Tomasović: Raspre i rasprave, Matica hrvatska, Zagreb 2012.
POVIJEST HRVATSKOGA JEZIKA - Identiteti međusobno
razumljivih jezika hr, sr, bs, me - hrvatski jezik
- Identities of mutually intelligible languages: Croatian, Serbian, Bosnian and Montenegrin (youtube)
- IDENTITIES of mutually intelligible languages - Croatian, Serbian, BS, ME, PART 2: historical survey (youtube)
- Identities of mutually intelligible languages: Croatian, Serbian, Bosnian and Montenegrin (archive.org)
- IDENTITIES of mutually intelligible languages - Croatian, Serbian, BS, ME, PART 2: historical survey (archive.org)
Svjedočanstva o hrvatskom identitetu Dalmacije
Renesansa u Dalmaciji, I
Renesansa u Dalmaciji, II
Croatia - an overview of its History, Culture and Science